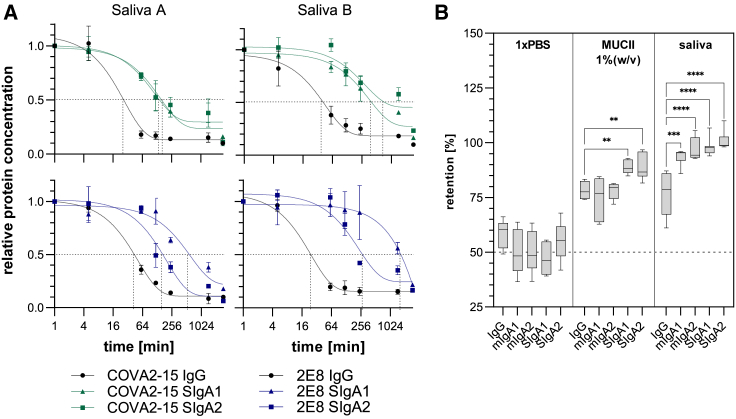
Figure 2.
Stability and interaction of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgA with mucus
(A) Saliva from 2 donors (Saliva A and Saliva B) was mixed with COVA2-15 and 2E8 IgG and SIgA mAb variants and incubated at 37°C for the indicated time. Samples were analyzed for binding to RBD and assembly through detection with Fc-specific and SC-specific antibodies. The mean ± SD of duplicates is shown. Gray dotted lines indicate half-lives of COVA2-15 and 2E8 variants calculated using a 1-phase decay nonlinear regression model. (B) COVA2-15 IgG and IgA mAbs were mixed with PBS, MUCII or human saliva and dialyzed against PBS using a 0.05-μm filter in a fast equilibrium microdialysis setup. mAb concentrations pre- and postdialysis were quantified via antigen sandwich ELISA. Data represent the mean of at least 4 repeats ± SEM. One-way ANOVA was performed to compare IgA groups with the IgG group; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.