Table 1.
Optimization study
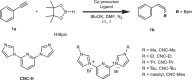 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Precursor | Ligand | Yield (%)a | Z/E ratiob |
| 1 | CoCl2 | CNC-H | 0 | – |
| 2 | CoCl2 | CNC-Me | 71% | 3:97 |
| 3 | CoCl2 | CNC-Et | 78% | 36:64 |
| 4 | CoCl2 | CNC-iPr | 99% | 2:98 |
| 5 | CoCl2 | CNC-tBu | 7% | <1:99 |
| 6 | CoCl2 | CNC-Mes | 0 | – |
| 7c | CoCl2 | CNC-iPr | 99% | 96:4 |
| 8d | CoCl2 | CNC-iPr | 70% | >99:1 |
| 9e | CoCl2 | CNC-iPr | 45% | 97:3 |
| 10e | Co(acac)2 | CNC-iPr | 98% | 51:49 |
| 11f | Co(acac)2 | CNC-iPr | 99% (90%)g | 98:2 |
| 12f,h | Co(acac)2 | CNC-iPr | 98% (90%)g | >99:1 |
Reaction conditions: CoCl2 (5.0 mol%), 1a (0.4 mmol, 1.0 equiv), ligand (5.0 mol%),
tBuOK (20.0 mol%), HBpin (3.0 equiv), DMF (2 ml), room temperature (r.t.), N2 atmosphere, 12 h.
aNMR yield determined using methylene bromide as the internal standard.
bZ/E ratio based on 1H NMR analysis.
cReacted for 10 min.
dHBpin used in 1.5 equiv., 24 h.
eCo precursor (0.2 mol%), ligand (0.22 mol%),
tBuOK(0.8 mol%), DMF (1 ml).
fCo(acac)2 (0.1 mol%), ligand (0.14 mol%),
tBuOK(0.56 mol%), DMF (0.5 ml).
gIsolated yield.
hHBpin (1.3 equiv.).
