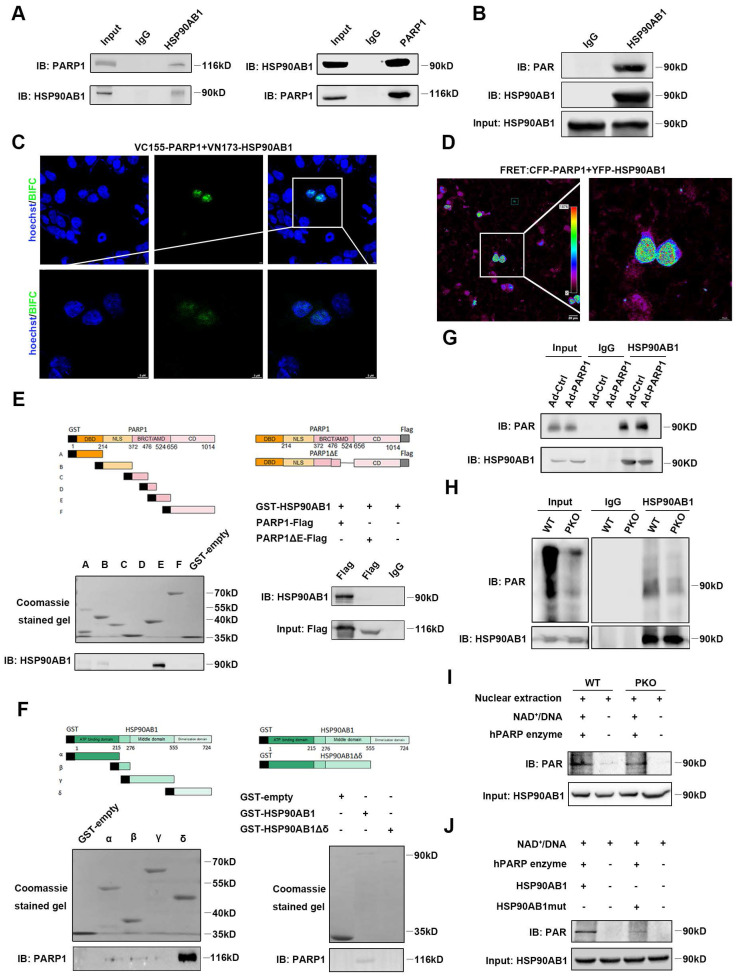
Figure 5.
PARP1 directly interacts with and poly(ADP-ribosyl)ates HSP90AB1 in cardiomyocytes. (A) Co-IP assay displayed the interaction of PARP1 and HSP90AB1 in NRCMs. (B) Co-IP assay showed the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of HSP90AB1 in NRCMs. (C and D) Representative images of BiFC and FRET assay showing the interaction of PARP1 and HSP90AB1. Scale bars, 10 μm (C) and 20 μm (D). (E) GST-pull down assay showed the interaction of PARP1-E domain and PARP1-E domain deletion mutant with HSP90AB1. (F) GST-pull down assay showed the interaction of HSP90AB1-δ domain (Left) and HSP90AB1-δ domain deletion mutant (Right) with PARP1. (G and H) Co-IP assay showed the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation level of HSP90AB1 in NRCMs transinfected with Ad-Ctrl or Ad-PARP1 and in nuclear extracts from WT and PKO mice. (I) Co-IP assay showed the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation level of HSP90AB1 in nuclear extracts from WT or PKO mice heart incubated with active DNA and NAD+, respectively. (J) Co-IP assay displayed the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation level of HSP90AB1 in HSP90AB1 and HSP90AB1mut purified protein incubated with active DNA and NAD+.