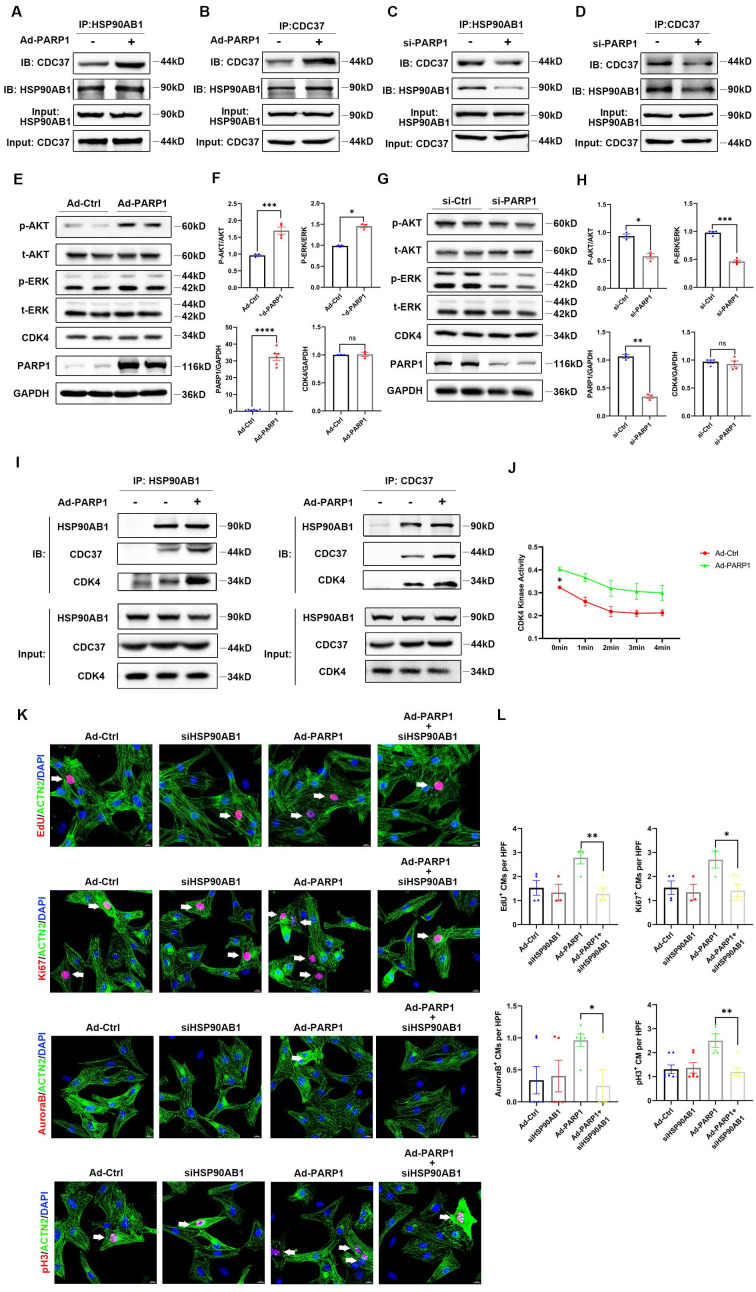
Figure 6.
PARP1 controls cardiomyocyte proliferation through HSP90AB1-CDC37 functional complex formation. (A and B) Co-IP assay showed the binding between HSP90AB1 and CDC37 in NRCMs infected with or without Ad-PARP1. (C and D) Co-IP assay showed the binding between HSP90AB1 and CDC37 in NRCMs infected with or without si-PARP1. (E and F) Representative western blot images and statistical analysis of protein expression of p-AKT/AKT, p-ERK /ERK, CDK4, PARP1, and GAPDH in NRCMs infected with Ad-Ctrl and Ad-PARP1 (n=3-6). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ***P < 0.001 by unpaired Student's t-test. (G and H) Representative western blot images and statistical analysis of protein expression of p-AKT/AKT, p-ERK /ERK, CDK4, PARP1, and GAPDH in NRCMs transfected with si-Ctrl and si-PARP1 (n=3-6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by unpaired Student's t-test. (I) Co-IP assay showed the interaction between HSP90AB1, CDC37, and CDK4 in NRCMs infected with or without Ad-PARP1. (J) Statistical analysis of CDK4 kinase activity in NRCMs infected with Ad-Ctrl and Ad-PARP1 at different time points (n=3). *P < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test. (K and L) Representative immunostaining images and statistical analysis of EdU+, Ki67+, Aurora B+, pH3+ cardiomyocytes (red) in Ad-Ctrl, si-HSP90AB1, Ad-PARP1, and Ad-PARP1+siHSP90AB1 NRCMs (n=3-7). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni test.