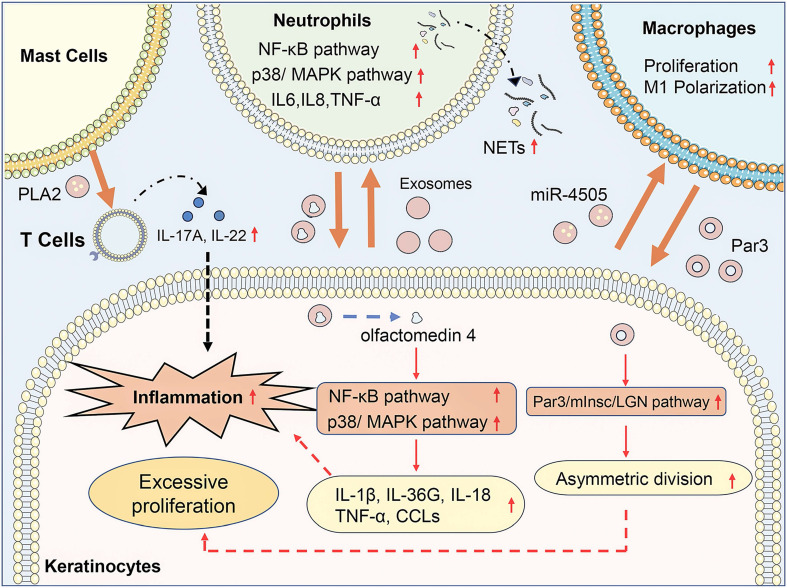
Figure 1.
Exosomes in psoriasis pathogenesis. In psoriasis, keratinocyte exosomes promote neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in neutrophils via activating the NF-κB and p38/MAPK pathway and promote their proliferation and M1 polarization of macrophages via transferring miR-4505. Neutrophil exosomes containing olfactomedin 4 activate NF-κB and MAPK pathway in keratinocytes to promote expression of IL-1β, IL-36G, IL-18, TNF-α, and C-X-C motif chemokine ligands (CCLs). Macrophage exosomes manipulated the asymmetric division of keratinocytes via activating the Par3/mInsc/LGN signaling pathway. Mast cell-released exosomes transferred cytoplasmic PLA2 to CD1a-reactive psoriatic T cells inducing the production of IL-22 and IL-17A in psoriasis patients. In conclusion, exosome-mediated communication between activated keratinocytes and infiltrated immune cells contributes to the progression of psoriasis.