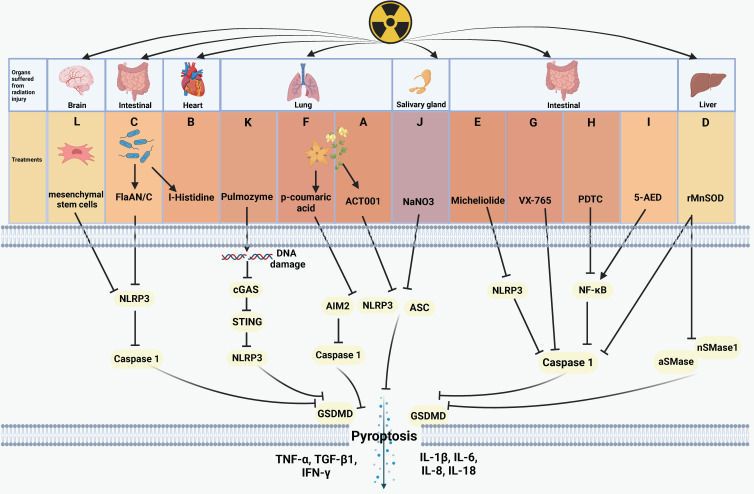
Figure 2.
Regulative mechanism of inhibitors for treating pyroptosis-related radiation injury. (A) The feverfew plant extract ACT001 inhibits NLRP3 and reduces the expression of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, and GSDMD, thereby inhibiting pyroptosis and radiation-induced lung injury. (B) I-Histidine, secreted by intestinal flora, mitigates radiation-induced cardiopulmonary injury by inhibiting pyroptosis. (C) Bacterial-derived FlaAN/C inhibits ROS, NLRP3, and caspase-1, thus attenuating intestinal cells pyroptosis and the release of inflammation-related cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-18, IL-8, IL-6, and TNF-α. (D) rMnSOD inhibits radiation-induced liver damage by inactivating caspase-1, aSMase, and nSMases. (E) Micheliolide inhibits the NLRP3/caspase-1 axis, attenuating pyroptosis and the release of cytokines including IL-1β, IL-18, TGF-β1, TNF-α, and IFN-γ, which ultimately promots mice survival after radiation exposure. (F) p-Coumaric acid inactivates caspase-1, NLRP3, and AIM2 to inhibit pyroptosis and radiation-induced lung injury. (G-H) VX-765 and the NF-κB inhibitor PDTC inhibit caspase-1 to alleviate radiation-induced intestinal damage. (I) 5-AED upregulates the expression of NF-κB to mitigate AIM2-driven pyroptosis and radiation-induced intestinal injury. (J) NaNO3 inhibits pyroptosis and acinar cells damage by downregulating the expression of NLPR3, ASC, GSDMD, IL-18, thus inhibiting pyroptosis. (K) Pulmozyme inhibits double-strand DNA damage and the the cGAS/STING/NLRP3 axis activation and the release of IL-1β, IL-18, protecting lung tissue from radiation damage. (L) Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit NLRP3 and caspase-1 to alleviate radiation-induced brain damage.