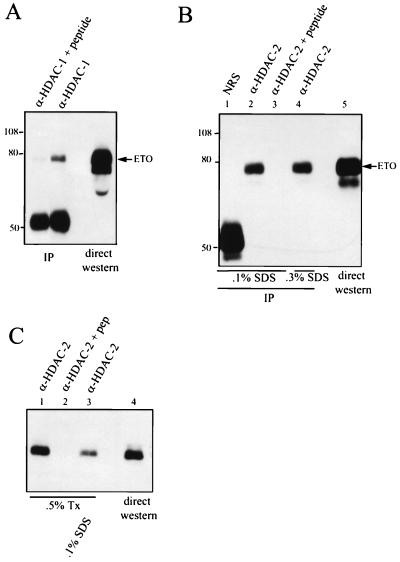
FIG. 5.
ETO interacts with HDACs. (A) ETO interacts with endogenous HDAC-1. Cos-7 cells were transfected with pCMV5-ETO, and cell extracts were prepared in PBS containing 0.5% Triton X-100 and immunoprecipitated with anti-HDAC-1 IgG in the presence or absence of the antigenic peptide. ETO was detected by immunoblot analysis using antibodies directed against the C terminus of ETO. IP, immunoprecipitation. (B) ETO interacts with endogenous HDAC-2. Cos-7 cells were transfected with pCMV5-ETO, and cell extracts were prepared in PBS containing 0.5% Triton X-100, 0.5% Na deoxycholate, and either 0.1% (lanes 1 to 3) or 0.3% (lane 4) SDS and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with 4 μg of anti-HDAC-2 IgG or anti-HDAC-2 IgG that had been blocked with 20 μg of antigenic peptide. Proteins were separated by SDS–8% PAGE prior to autoradiography. NRS, normal rabbit serum. Note that the anti-HDAC-2 is a goat polyclonal antibody and is not detected by the anti-rabbit secondary antibody. (C) Endogenous ETO interacts with endogenous HDAC-2. HEL cell lysates were prepared in PBS containing 0.5% Triton X-100 (Tx) with or without 0.1% SDS and immunoprecipitated with anti-HDAC-2 IgG. The presence of ETO in immune complexes was detected by immunoblot analysis using anti-ETO IgG. Twenty-fold more extract was used for immunoprecipitation than was analyzed by direct immunoblotting. The values on the left of panels A and B are molecular sizes in kilodaltons.