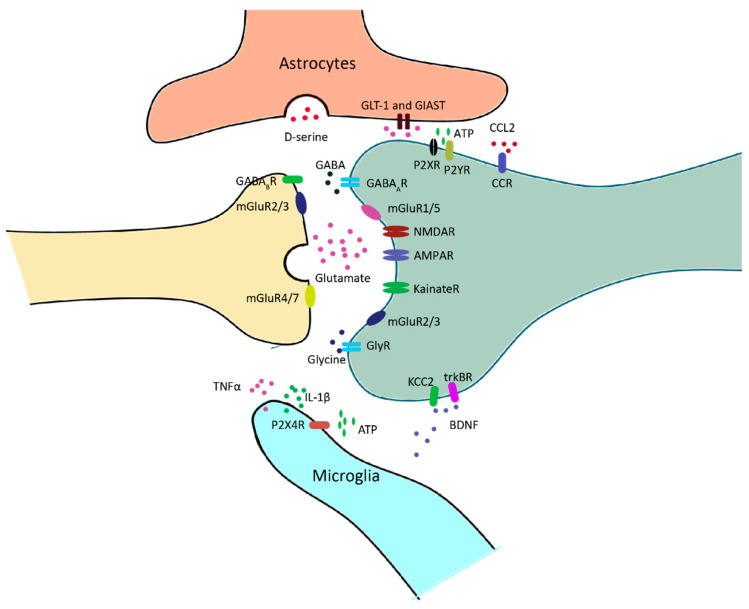
Figure 3.
Neuron–glia interactions at nociceptive synapses in the spinal dorsal horn (SDH). Glutamate or GABA/Glycine is released upon the arrival of action potential at the presynaptic fiber. GABA and glycine receptors mediate inhibitory transmission, and glutamatergic receptors mediate excitatory transmission. Ionotropic glutamate receptors, including AMPA receptors, NMDA receptors and kainate receptors, are mainly located in the postsynaptic domain. Metabotropic glutamate receptors are located in both the pre- and postsynaptic domains. Excessive glutamate is taken up by astrocytes and converted to glutamine for the synthesis of glutamate. In response to neuropathy, microglia release a series of inflammatory factors, such as TNFα and IL-1β, which modulate the activity of neurons via a neuro-immune interaction. BDNF is also released by microglia, and it affects neuronal excitability by regulating Cl- homeostasis.