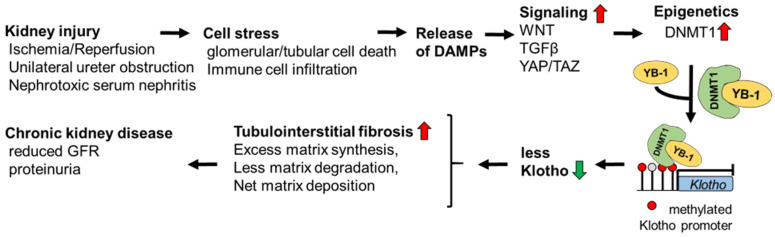
Figure 9.
Proposed model summarizing the YB-1-dependent regulation of Klotho expression leading to chronic kidney disease. Cell stress induces the release of DAMPs, triggering WNT, TGFβ, and YAP/TAZ signaling, followed by enhanced expression of DNMT1, a protein that regulates epigenetics. The cytosolic complexes of YB-1 and DNMT1 translocate to the nucleus and bind to the Klotho promoter region. This leads to promoter hypermethylation with reduced Klotho expression. Enhanced tubulointerstitial fibrosis ensues. The deletion of YB-1 in kidney-resident cells reverses the hypermethylation of Klotho together with reduced WNT, TGFβ, and YAP/TAZ signaling. (⇧ red, enhanced activation; ⇩ green, reduced expression)Several limitations exist for our data analyses and interpretation. Our bulk sequencing data and chip-on-chip data sets should be extended by single-cell analyses. Only murine models of kidney disease have been incited. The conclusions must be transferred to the human situation and tissue analyses. It remains unclear whether the mechanisms obtained in Figure 9 apply to all cell types or are cell-specific.