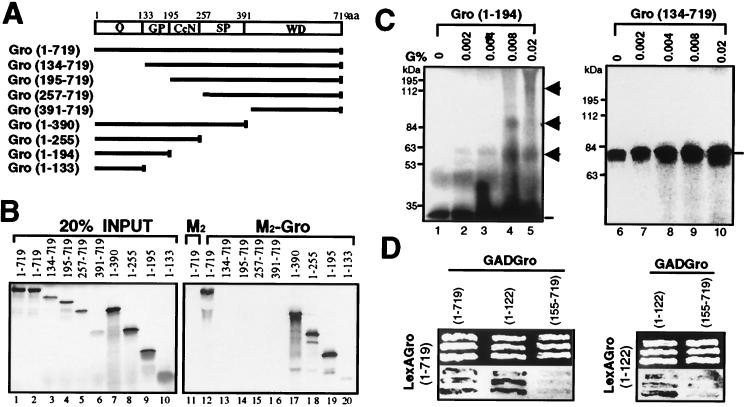
FIG. 3.
Mapping the tetramerization domain of Gro. (A) Schematic diagram of various full-length or truncated [35S]methionine-labeled Gro proteins that were produced by in vitro translation. The conserved N-terminal glutamine-rich domain (Q) and C-terminal WD repeat domain (WD) are indicated. GP and SP, glycine-proline and serine-proline, respectively, which are predominant in these regions; CcN, CcN motif containing putative cdc2 and casein kinase II phosphorylation sites as well as a nuclear localization signal (44); aa, amino acids. (B) In vitro coimmunoprecipitation assays. Purified FLAG-tagged Gro (1 μg) (M2-Gro) immobilized on anti-FLAG affinity resin was incubated with 10 μl of each of the 35S-labeled Gro variants. Lanes 1 to 10 show an amount of each input protein equal to 20% of the amount used in the binding reactions shown in lanes 11 to 20. After being extensively washed, the bound 35S-Gro was eluted with SDS-PAGE sample buffer, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography (lanes 12 to 20). As a negative control, the anti-FLAG affinity bead (M2) alone was examined for interaction with full-length 35S-Gro (11). (C) Cross-linking analysis of truncated 35S-Gro proteins. Cross-linking reactions conducted as described in the legend to Fig. 2B were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The left and right panels show the cross-linking profiles of 35S-labeled Gro(1–194) and Gro(134–719), respectively. The percent glutaraldehyde (G%) used in the cross-linking reactions is shown above the lanes. The 35S-Gro monomers are indicated by lines, and cross-linked dimer, trimer, and tetramer species are indicated by arrowheads. The sizes of prestained protein markers are indicated on the left. (D) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of Gro oligomerization. The top panels show three independent yeast colonies cotransformed with the LexA DNA binding domain-Gro fusion proteins (LexAGro, indicated on the left of each panel) and GAD-Gro fusion proteins (GADGro, indicated on the top of each panel). The bottom panels show the results of growing these colonies in the presence of the chromogenic β-galactosidase substrate X-Gal. Cells expressing β-galactosidase turn blue.