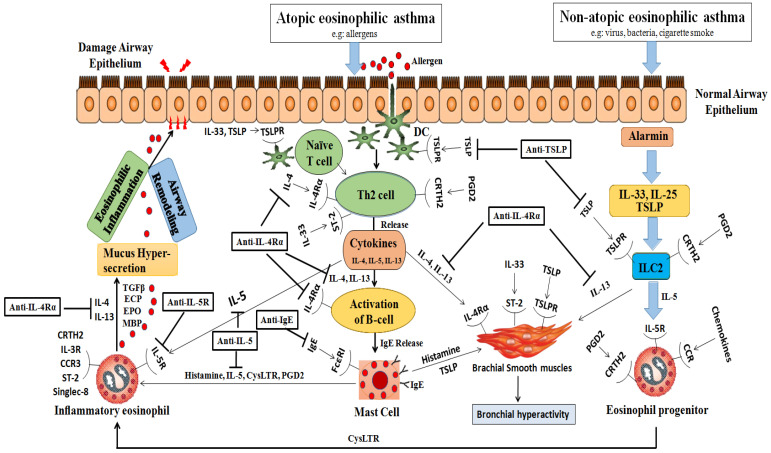
Figure 1.
Immunopathology of eosinophilic asthma and targets of biological. This figure illustrates the immunological processes involved in eosinophilic asthma, highlighting the differences between the atopic and nonatopic variants: Atopic Eosinophilic Asthma: Initial step: allergens penetrate the airway epithelium after exposure; dendritic cells (DCs): capture these allergens and facilitate the differentiation of Th2 cells; Th2 cell differentiation: leads to the release of multiple cytokines, notably IL-4; IL-4’srole: stimulates B cell activation, leading to IgE release; mast cells: respond by initiating degranulation and releasing histamine, IL-5, cysteinyl leukotrienes (CysLTRs), and prostaglandin D2 (PGD2); eosinophil degranulation: triggered by mast cell factors and further enhanced by IL-4 and IL-13 from the Th2 cells. Nonatopic Eosinophilic Asthma: Alarmins: IL-25, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) interact with the type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) via the CRTH2 receptor; significance of IL-5: this interaction is crucial, particularly in the presence of IL-5 cytokines, leading to the activation or degranulation of eosinophils. Common Outcomes for Both Types: Mucus hypersecretion: augmented due to the combined effects; airway remodeling and eosinophilic inflammation: result of the synergistic action of the described processes; detrimental effects on the airway epithelium: caused by the released interleukins (IL-4, IL-13), eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), eosinophil peroxidase (EPO), and major basic protein (MBP). Abbreviations: EOS: eosinophil; DC: dendritic cell; TSLP: thymic stromal lymphopoietin; CysLTR: cysteinyll leukotriene; PGD2: prostaglandin D2; ILC2: type 2 innate lymphoid lcell; ECP: eosinophil cationic protein; EPO: eosinophil peroxidase; MBP: major basic protein; CRTH2: chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on Th2 cells; TSLPR: TSLP receptor.