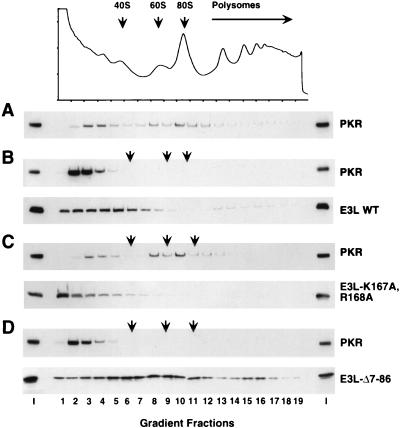
FIG. 10.
Expression of E3 displaces PKR from ribosomes in a manner that depends on the dsRNA binding activity of E3 but not its N-terminal domain. Transformants of strain J82 (expressing eIF2α-S51A) containing PKR plasmid p1545 and either a plasmid encoding wild-type E3 (p2245), E3-K167A,R168A (p2612), or E3-Δ7-86 (p2246) (B to D) or the empty vector p1079 (A) were grown in SGal medium to an OD600 of ≈1.5. Whole-cell extracts prepared in the presence of 50 mg of cycloheximide per ml and 10 mM MgCl2 were resolved by velocity sedimentation on 5 to 47% sucrose gradients. The gradients were fractionated, and absorbance at 254 nm was recorded to determine the position of the free 40S and 60S subunits, 80S monosomes, and polysomes (indicated by arrows). The OD254 absorbance profile is shown for the gradient analyzed in panel A; the OD254 profiles for panels B to D were essentially identical to that shown in panel A. The distribution of proteins along the gradients was visualized by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis. The first and last lanes in each panel were loaded with 1/20 of the input (I) extracts applied to the gradients.