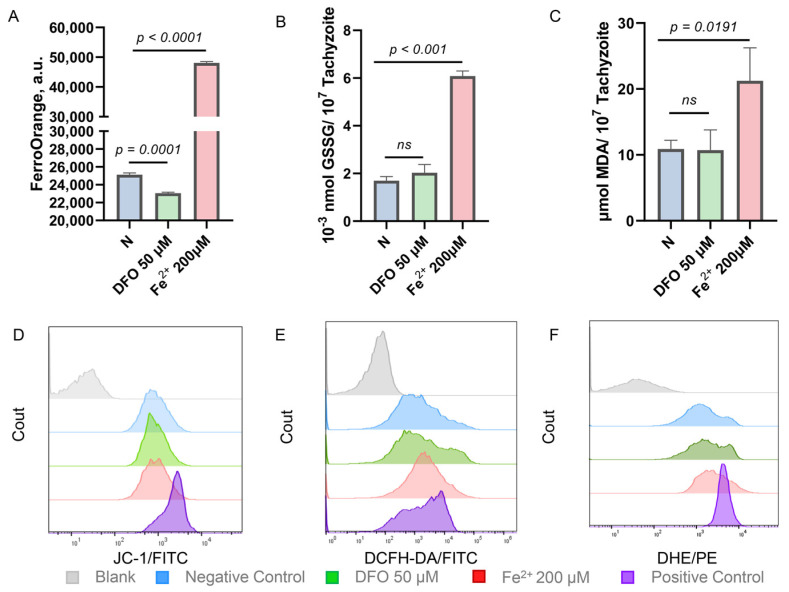
Figure 2.
Impact of iron accumulation on Toxoplasma redox capacity. (A) The fluorescence intensity of the fluorescent probe FerroOrange reflects changes in iron levels of T. gondii under conditions of iron depletion and iron accumulation. Iron chelating agents reduce parasite iron levels, while iron supplements increase them. Means ± SD of three independent experiments, each with three replicates, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. (B,C) The detection of oxidation products GSSG and MDA in T. gondii under different iron levels. Under iron accumulation, the content of parasite oxidation products increases. Means ± SD of three independent experiments, each with three replicates, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test, ns: non-significantly. (D–F) The analysis of changes in mitochondrial membrane potential (JC-1), ROS level (DCFH-DA), and superoxide anion concentration (DHA) in T. gondii under iron depletion (green) and iron accumulation (red). High iron levels increase ROS and superoxide anions but do not alter mitochondrial membrane potential.