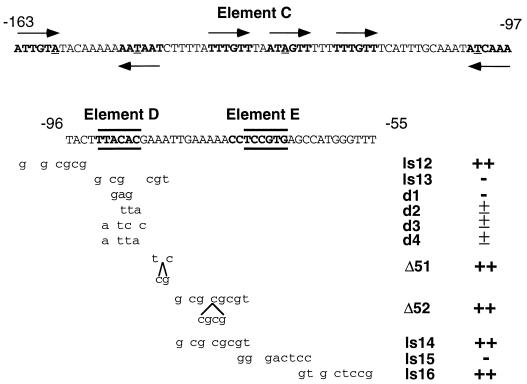
FIG. 4.
Nucleotide sequences of elements C, D, and E and additional alleles of element D. Element C, which is defined primarily by insertion-scanning mutations (see Table 3), is a large region that contains six sequences (boldface letters with arrows indicating orientation) that strongly resemble consensus recognition sites for Mc and other DNA-binding domains that contain the HMG structural motif (8, 10); underlined bases deviate from the consensus. The most critical bases of elements D and E are shown in boldface letters and are bracketed by horizontal lines. Shown below are the structures (mutated base pairs are indicated in small letters) and phenotypes of the relevant mei3 derivatives used to define these elements. Derivatives d1 to d4 were designed to assess whether element D is recognized by Pm in vivo (see Fig. 6).