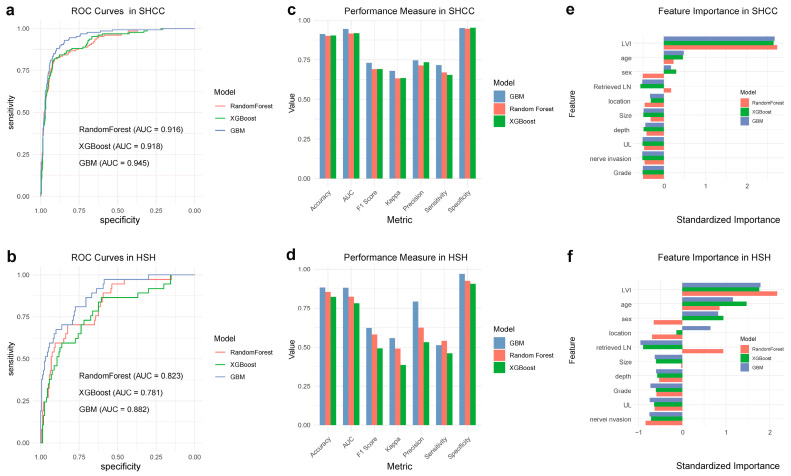
Figure 2.
Comparative performance of predictive algorithms for assessing the prognostic significance of LVI in predicting LNM within EGC patients across two centers. (a,b) ROC Curves depicting the performance of Random Forest (RF), eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), and Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM) algorithms in SHCC (Shanghai Cancer Center) (a) and HSH (Huashan Hospital) (b). The Area Under the Curve (AUC) values are specified for each model. (c,d) Performance metrics comparison of the RF, XGBoost, and GBM algorithms, encompassing accuracy, AUC, F1 score, Kappa statistics, precision, sensitivity, and specificity in both SHCC (c) and HSH (d). (e,f) Feature importance plots for RF, XGBoost, and GBM algorithms, demonstrating the relative significance of different predictors, with LVI consistently emerging as a paramount predictor for LNM in both SHCC (e) and HSH (f).