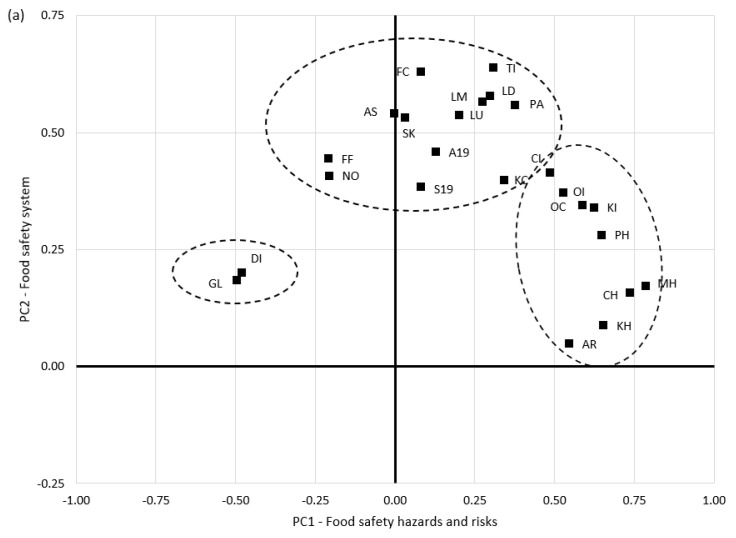
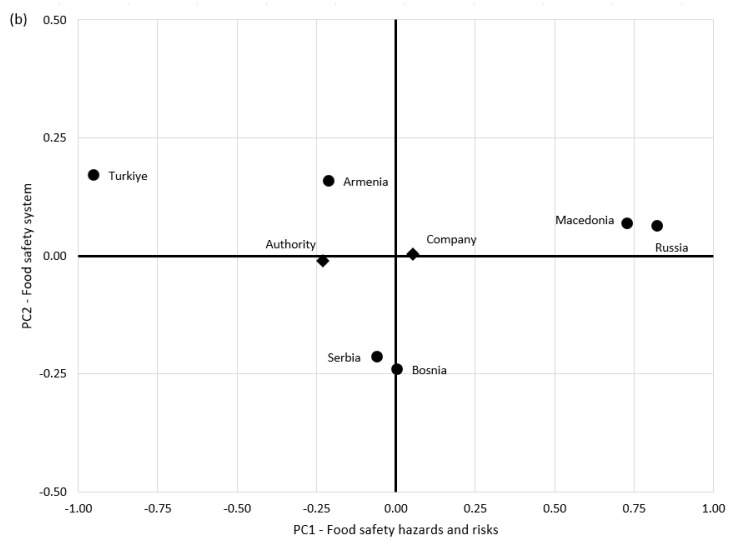
Figure 2.
Principal component analysis loadings (a) and scores (b) plots for the 24 statements deployed by type of respondents and country. Rotation method: Varimix. Statements: (■) Legislation is up to date—LD; Legislation is understandable—LU; Proactive approach—PA; Transparently share information—TI; Knowledge among food inspection services—KI; Knowledge among food handlers—KH; Knowledge among food consumers—KC; Outbreak investigation—OI; Outbreak communication—OC; Assessment/audit services—AS; Scientific knowledge—SK; Laboratory methods—LM; System change in COVID-19—S19; Authority change in COVID-19—A19; Microbial hazards—MH; Chemical hazards—CH; Physical hazards—PH; Antimicrobial resistance—AR; Food fraud—FF; Food safety culture—FC; Continually improving—CI; New distribution channels—DI; Globalization of trade—GL; Novel food technologies—NO. Respondents (♦)—food company and food safety authority; Country (●)—Armenia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, North Macedonia, Russia, Serbia, Türkiye.