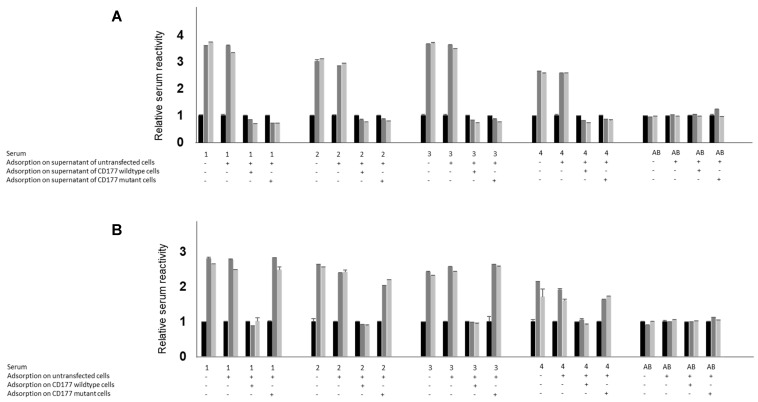
Figure 4.
Analysis of anti-HNA-2 isoantibodies reactivity with immobilised CD177 (wildtype or c.1291A mutant) protein in ELISA. Proteins from cell culture supernatants of transfected cells, either mock (black), wildtype (dark grey), or mutant (light grey), were immobilised on V5-pre-coated microtiter plate. Before adding to immobilised protein, sera were first incubated with supernatant obtained from untransfected HEK293F cells (−/−), followed by adsorption to supernatant from HEK293F cells expressing CD177 wildtype (−/+G) or supernatant from CD177 c.1291A mutant (−/+A). After washing, human serum containing anti-CD177 antibodies (from CD177 c.787T individuals) or control serum (as negative control) was added. Bound human IgGs were detected using horseradish-labelled goat anti-human IgG. (A) To differentiate the reactivity of human antibodies against CD177 wildtype and mutant expressed on cell surface, sera were first incubated with untransfected HEK293F cells (−/−), followed by adsorption to HEK293F cells expressing either CD177 wildtype (−/+G) or CD177 c.1291A mutant (−/+A). In similar experiments, adsorption of human antibodies to proteins present in supernatant was conducted (B). The adsorbates were added to immobilised CD177 protein (either mock (black), wildtype (dark grey), or mutant (light grey)) and bound human IgG was detected using horseradish peroxidase-labelled goat anti-human IgG, (n = 4). Values are presented as mean ± SD (n = 5) (cut-off determined for supernatant ELISA was 1486 as determined with sera from non-immunised healthy donors with blood group AB (n = 20). The statistical significance of the difference in adsorption between mutant and wild-type CD177 was analysed by ANOVA using GraphPad Prism 7.