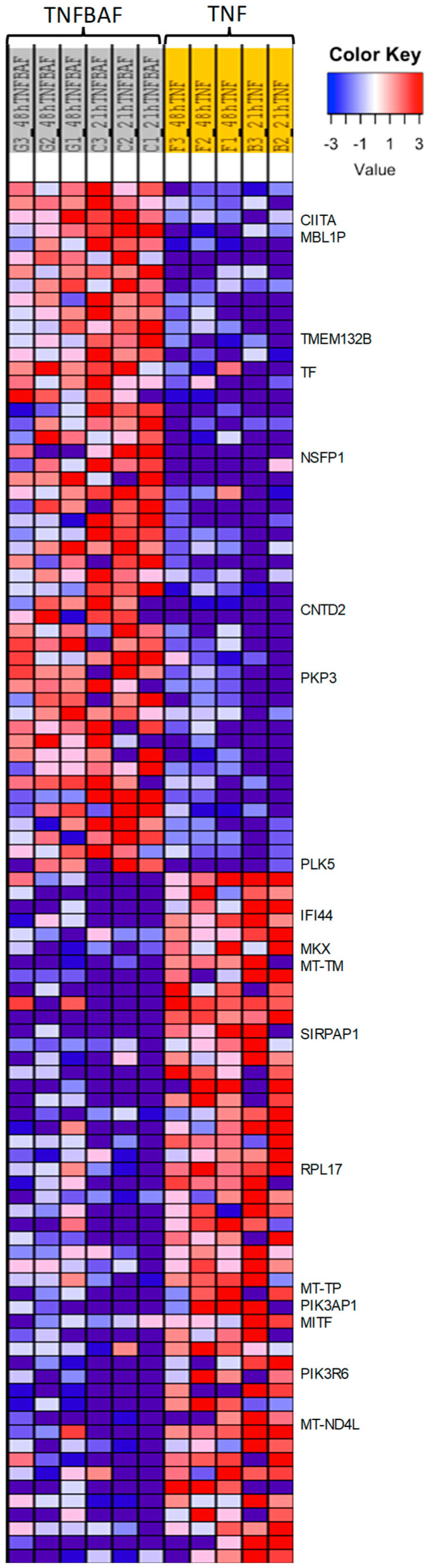
Figure 8.
Heatmap of gene expression shows that siponimod/BAF312 treatment reverses TNFα-driven neuroinflammation in oxidative phosphorylation, apoptosis, MAPK/NFKB signaling, and cytokine to cytokine receptor interaction pathways in human neuronal hiPSCs-NSCs/NPCs cells. Heatmap shows differential expressed genes with siponimod/BAF312 treatment with TNFα as compared to TNFα alone in hiPSCs-NSCs/NPCs cells. Downregulated genes are shown in blue and upregulated genes are in red. Genes of interest are marked on the right, including genes involved in mitochondrial metabolic and inflammatory functions [MT-ND4L, a core subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I), which catalyzes electron transfer from NADH through the respiratory chain, using ubiquinone as an electron acceptor; MT-TM, the mitochondrially encoded tRNA methionine that transfers the amino acid methionine to a growing polypeptide chain at the ribosome site of protein synthesis during translation causing neuromuscular disorder mitochondrial myopathy; TMEM132B, a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in the brain cortex and immune cells; and TF, where the transferrin is an iron-binding transport protein that is responsible for the transport of iron from sites of absorption and heme degradation to those of storage and utilization. Serum transferrin may have a role in stimulating cell proliferation as a growth factor that is involved in stem cell differentiation protocols towards the derivation of the following cells, like in neurons’ neural precursor-like cells, motor neuron progenitor cells, and motor neuron-like cells; PIK3AP1, the phosphoinositide-3-kinase adaptor protein 1 involved in the regulation of inflammatory response, regulation of signal transduction, and Toll-like receptor signaling pathway; MITF, a microphthalmia-associated transcription factor that regulates the expression of genes with essential roles in cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival; RPL17, the ribosomal protein L17 that is involved in peptide chain elongation and metabolism pathways; PIK3R6, a phosphoinositide-3-inase regulatory subunit 6 that is involved in metabolism pathways; MT-TP, Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein, plays a central role in lipoprotein assembly; CIITA is class II major histocompatibility complex transactivator involved in the common mechanism of immune escape through reduction of MHC class II expression in primary mediastinal large B cell lymphoma; SIRPAP1 is signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα), a regulatory membrane glycoprotein from SIRP family expressed mainly by myeloid cells and also by stem cells or neurons; PLK5 is Polo Like Kinase 5 (Inactive) that is predicted to enable ATP binding activity and protein kinase activity involved in several processes, including defense response to tumor cell; positive regulation of neuron projection development; and regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle; PKP3 (Plakophilin 3) expressed in dendritic reticular cells of lymphatic follicles; MKX (Mohawk Homeobox) is a transcription factor that promotes meniscus cell phenotype and tissue repair and reduces osteoarthritis severity. Smad3 binds it; IFI44 (Interferon Induced Protein 44) is an immune evasion biomarker for SARS-CoV-2 and Staphylococcus aureus infection and associated with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome; CNTD2 (cyclin N-terminal domain containing 2) is involved in sphingolipid metabolism; NSFP1 (N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor pseudogene 1) is widely expressed in brain tissue]. n = 5–6 pairs.