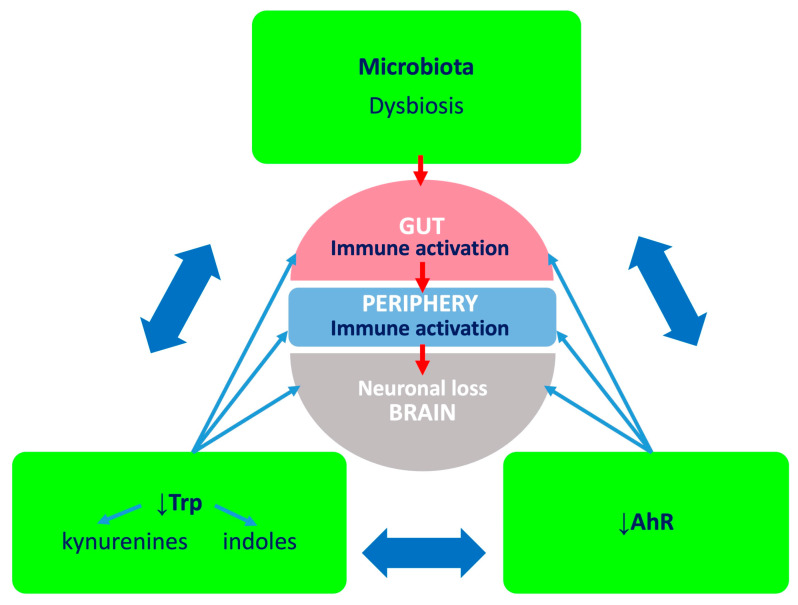
Figure 3.
Microbiota, tryptophan (Trp), aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) triad and the microbiota–gut–brain axis. Dysbiosis may affect Trp metabolism in the gut and the production of AhR ligands. Ensuing pro-inflammatory environment impacts intestinal enterocytes, and cytokines and chemokines evoke inflammation in situ. Furthermore, when absorbed into the systemic circulation, inflammatory molecules affect peripheral organs and the brain. Deficiency of Trp and AhR ligands further exacerbates inflammation. This, together with the disturbed metabolic conversion of Trp and shift from neuroprotective to neurotoxic kynurenines, will contribute to cytotoxicity.