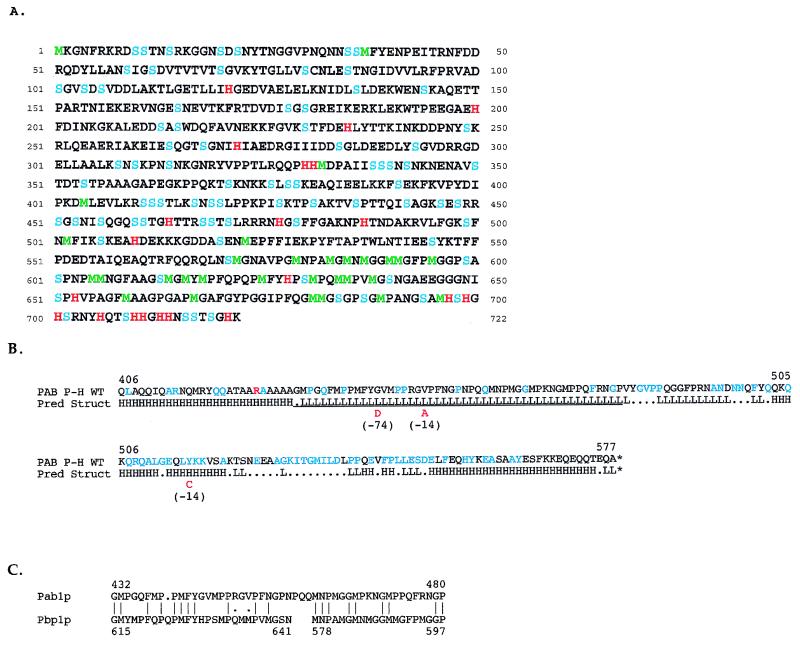
FIG. 2.
Structural features of Pbp1p and Pab1p. (A) Amino acid sequence of Pbp1p deduced from the sequence of the PBP1 gene. Histidine (H) is in red, methionine (M) is in green, and serine (S) is in blue. (B) Structural features of the Pab1p bait fragment. Pred Struct, predicted structure. H and L denote helical and loop regions, respectively, as predicted by the nnpredict program (39). Dots indicate residues for which no prediction was made. WT, wild type. Amino acids in blue are those with a strong evolutionary conservation among Pab1p homologs of eight different species (45a). The underlined segment corresponds to the region of Pbp1p homology shown in panel C. Amino acids in red denote substitutions found in two lexA(DB)-pab1 P-H alleles that were incapable of promoting a detectable two-hybrid interaction with GAL4(AD)-PBP1 (198–722). Mutant M(−74) has a single G→D substitution, and mutant M(−14) has both V→A and Y→C substitutions. The red R at position 426 denotes an A→R substitution in the bait fragment relative to the published sequence of PAB1 (61). (C) Alignment of homologous C-terminal regions of Pab1p and Pbp1p. Vertical lines indicate identity; dots denote similarity.