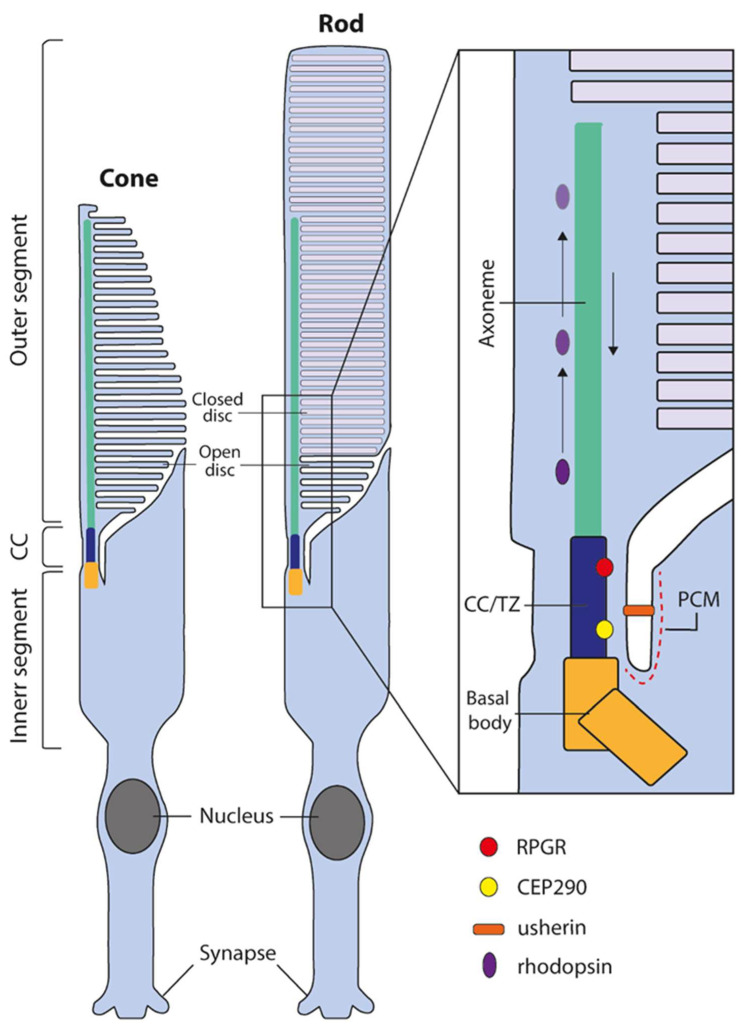
Figure 1.
The structure of human cone and rod photoreceptors and connecting cilium. Both cone and rod photoreceptors are divided into two distinct sections, the inner segment, and the disc containing outer segment. The region connecting these distinct compartments is known as the connecting cilium or transition zone (CC/TZ). The outer segment lacks the capacity for protein synthesis and is dependent on protein trafficking across the CC/TZ and subsequent transport along the distal axoneme. Numerous proteins are required for cilial function and maintenance, such as RPGR and CEP290 localized in the CC/TZ or usherin located in the periciliary membrane (PCM). Black arrows depict anterograde and retrograde cilial transport.