FIGURE 2.
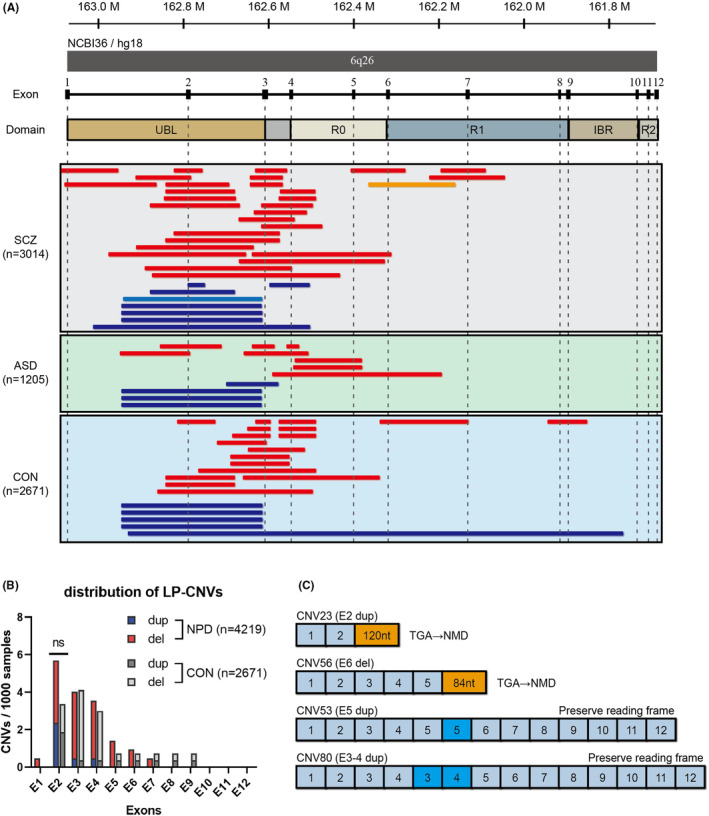
Genomic locations, distribution, and consequences of LP‐CNVs in PRKN. (A) Genomic locations of LP‐CNVs in PRKN. Red bars and dark blue bars represent deletions and duplications identified in the monoallelic carriers, respectively. The yellow bar and light blue bar represent the deletion (CNV56) and the duplication (CNV23) identified in the biallelic carrier. The genomic coordinates correspond to the NCBI36/hg18 build of the human genome assembly. (B) Distribution of LP‐CNVs in the 12 exons of PRKN in NPD cases (n = 4219) and controls (n = 2671). (C) Predicted consequences of the mRNA structure due to CNVs in PRKN. Duplication or deletion disrupting reading frames and resulting in a premature stop codon that leads to NMD (e.g., CNV23 and CNV56). Duplication spanning one or more exons preserving reading frames and leading to mRNA with exon repetition (e.g., CNV53, and CNV80). ASD, autism spectrum disorder; CON, healthy controls; LP‐CNV, likely pathogenic copy number variation; del, deletion; dup, duplication; NMD, nonsense‐mediated mRNA decay; NPD, neuropsychiatric disorder; nt, nucleotide; SCZ, schizophrenia.
