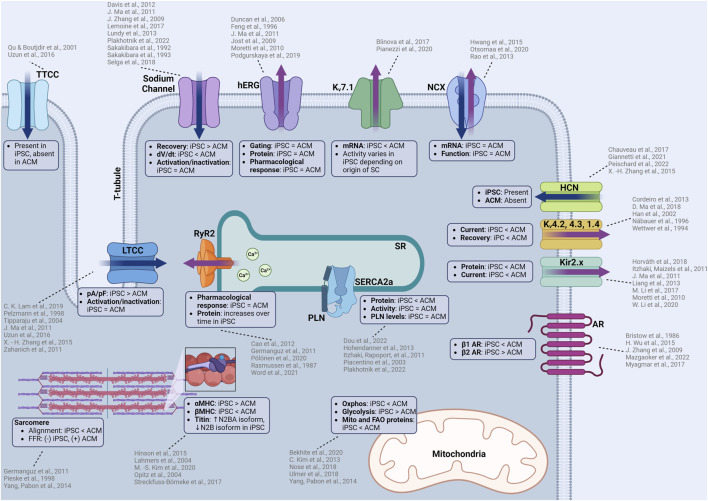
FIGURE 1.
Summary of functional similarities and differences between iPSC-CMs and adult human CMs (ACM). iPSC-CMs are similar in many aspects including electrophysiology, calcium handling, contractile machinery which allows the use of iPSC-CMs to predict cellular responses to novel compounds. However, there are some differences that must be considered when considering iPSC-CMs as a model for cardiotoxicity testing. Some of these differences include ion channel kinetics, upstroke velocities, structural differences in the contractile machinery, isoform of proteins, and metabolic function. TTCC: T-type calcium channel, LTCC: L-type calcium channel, hERG: human-ether-a-go-go (rapid delayed rectifier potassium channel), Kv7.1: slow delayed rectifier postassium channel, NCX: sodium calcium exchanger, HCN: hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide gated channel, Kv4.2, 4.3, 1.4: voltage dependent potassium channels responsible for the transient outward current, AR: adrenergic receptor, RyR2: ryanodine receptor, SERCA2a: sarcoendoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase, PLN: phospholamban, Oxphos: oxidative phosphorylation, MHC: myosin heavy chain. Created with www.biorender.com.