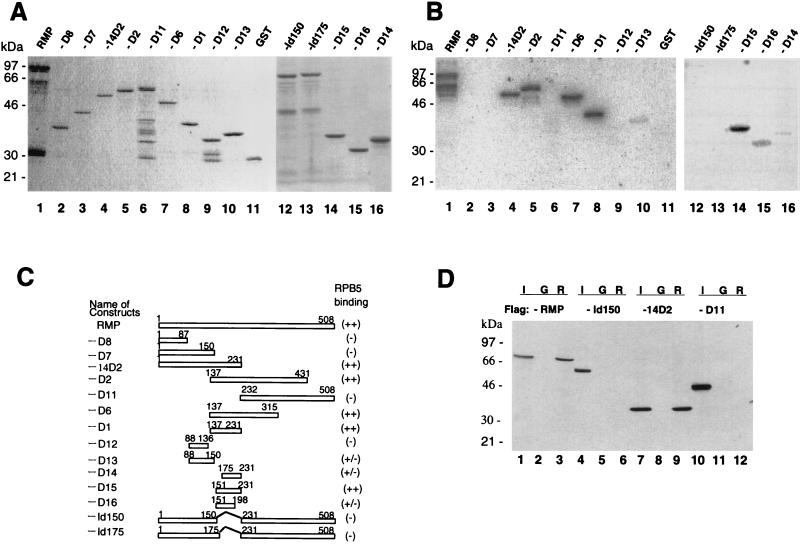
FIG. 4.
Delineation of the RPB5-binding region of RMP. (A) Coomassie brilliant blue staining of the fractionated full-length and truncated RMPs in GST-fused forms. (B) GST-RMP and truncated mutant proteins were subjected to far-Western blot analysis with a GST-RPB5 probe as described in the legend to Fig. 3. (C) Map of various RMP deletion constructs. The expression plasmids were constructed as described in Materials and Methods. The sequences encoding RMP-D1, -D2, -D6, -D11, -D12, and -D14 have an initiation codon followed by codons for various fragments of RMP. RMP-Id150 and RMP-Id175 have an internal deletion from aa 150 to 231 and from 175 to 231, respectively. The relative RPB5-binding abilities detected by far-Western blot analysis in panel B are shown at the right. (D) GST resin pull-down assay. Bacterially expressed FLAG-tagged full-length RMP and truncated mutants RMP-Id150, -14D2, and -D11 were incubated with GST (G) or GST-RPB5 (R). Approximately 1 μg of GST or GST-fused protein immobilized on glutathione resin was incubated with 100 ng of partially purified, bacterially expressed FLAG-RMP in GBT buffer for 2 h at 4°C. After being washed extensively, the bound proteins were eluted, fractionated by SDS–12.5% PAGE, and Western blotted with anti-FLAG M2 antibody. Lanes 1, 4, 7, and 10 show 5% of the input (I).