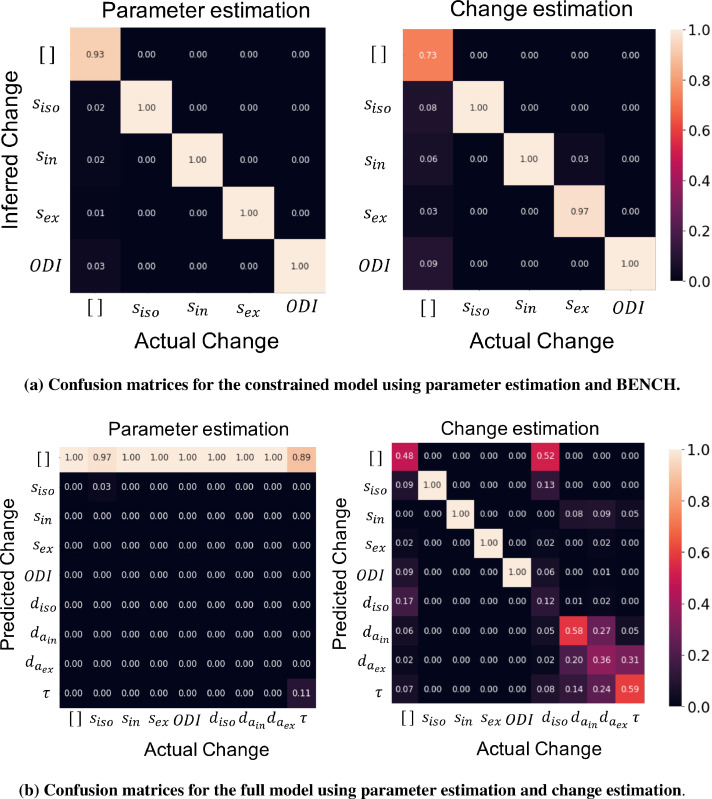
Fig. 8.
a) The numbers indicate the percentage of time a change in the corresponding column is identified as a change in the corresponding row. The diagonal elements show the accuracy in identifying true change. a) Both of the approaches performed near to ideal in detecting the true change in the case of constrained model. The change estimation has more false positives, but unlike the inversion approach, we did not explicitly define a false positive rate threshold. b) Given diffusion data at few shells, the full model is not invertible, i.e. the parameter estimates have a high variance. Therefore, almost no significant change is detected using parameter estimates. On the other hand, the change estimation approach can still identify changes in all the parameters of the restricted model. Although there remains confusion between a subset of the parameters since these have similar effects on the diffusion signal.