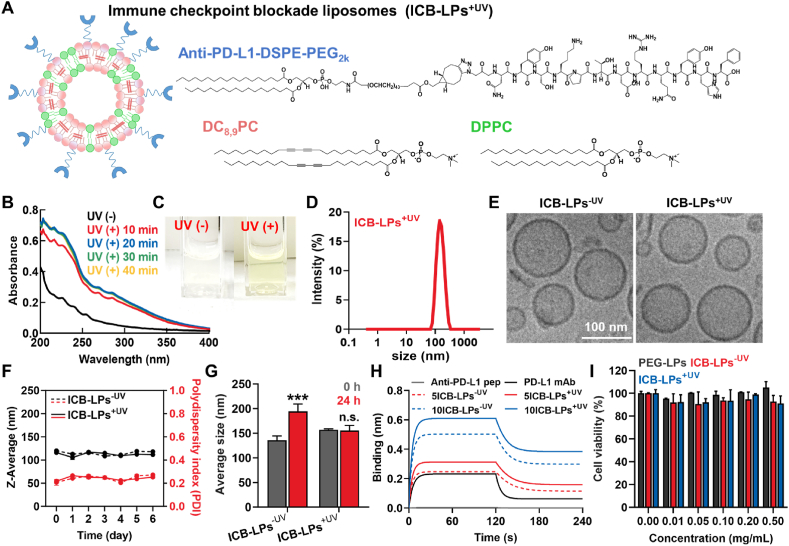
Figure 1.
Preparation and Characterization of ICB-LPs+UV. (A) The detail composition of ICB-LPs+UV. The ICB-LPs are prepared by formulation of DC8,9PC, DPPC anti-PD-L1-DSPE-PEG2k in a molar ratio of 45:45:10. (B) UV–Vis spectrum of ICB-LPs upon different time (10, 20, 30 and 40 min) of UV exposure. (C) Optical images of ICB-LPs before and 10 min after UV irradiation. (D) Size distribution of ICB-LPs+UV in saline (1 mg/mL). (E) Cryo-TEM images of ICB-LPs–UV and ICB-LPs+UV in distilled water (1 mg/mL). (F) The size and polydispersity index (PDI) of ICB-LPs–UV and ICB-LPs+UV in saline (1 mg/mL) for 6 days (n = 5). (G) The size of ICB-LPs–UV and ICB-LPs+UV after 0 or 24 h of incubation in mouse serum (1 mg/mL) condition (n = 5). (H) Binding kinetics on PD-L1-derivatized biosensors of anti-PD-L1 peptide, PD-L1 mAb and 5 or 10 mol%-incorporated ICB-LPs before and 10 min after UV irradiation. The concentration of anti-PD-L1 peptide, PD-L1 mAb and anti-PD-L1 peptide in each ICB-LPs was unified as 0.067 μmol. (I) The viability of CT26 cells after 48 h of treatment with PEG-LPs, ICB-LPs–UV and ICB-LPs+UV (n = 5). Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 5); n.s., P > 0.05, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. Control or indicated.