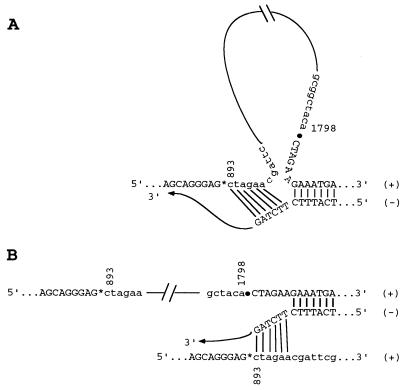
FIG. 10.
Two possible models of illegitimate recombination during minus-strand synthesis as exemplified for variant moHgag c1. Both models require a partial dissociation of the nascent minus [(−)] strand from the template plus [(+)] strand, caused by pausing of the polymerase. The free 3′ end of the nascent strand can reanneal to a short complementary sequence further upstream on the same template strand, thereby looping out the intervening sequences (A), or can reanneal to the same complementary sequence, but on a sibling plus strand, and complete synthesis on this second template (strand switching [B]). In both cases, the resulting minus strands would have excised the sequence between nt 893 and 1798 and can now, in turn, give rise to truncated positive-sense RNA genomes.