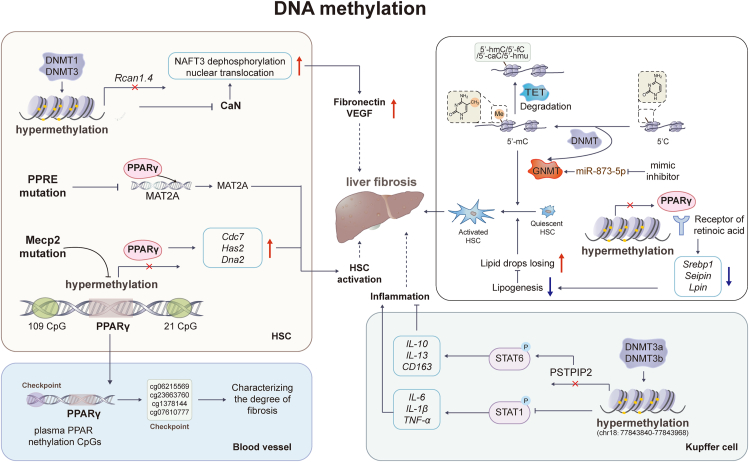
Figure 2.
The modulation of DNA methylation in liver fibrosis. Advances have been made in the understanding of the roles of DNA methylation in liver fibrosis. It has been observed that a repressive chromatin structure in exons can lead to gene transcription suppression through the addition of a methyl group at the 5′ position of cytosine. This process is mediated by the DNMT and GNMT family. Several genes, including PPARγ, RCAN1.4, and PSTPIP2, and methylated binding protein Mecp2 have been found to experience DNA methylation, and their transcriptional suppression has been shown to be closely related to the transactivation of HSCs and liver fibrosis.