Figure 4.
Charge reversal explains the correlation between divalent ion effects on Ddx4N0-N4 phase separation and protein net charge
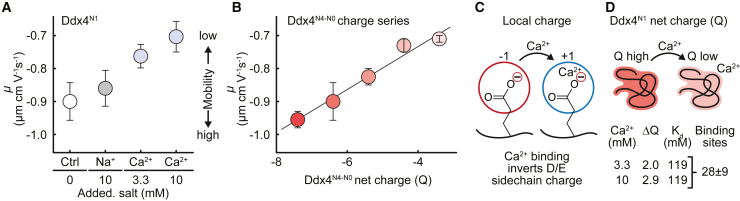
(A) Addition of CaCl2 lowers the electrophoretic mobility () of Ddx4N1 toward 0. Error bars indicate the SD.
(B) Standard curve of created with the Ddx4N0-N4 charge series. Error bars indicate the SD.
(C) Upon binding, the valency mismatch between a divalent Ca2+ ion and a negatively charged D (Asp) or E (Glu) sidechain leads to a reversal in charge from negative (−1) to positive (+1). This change in sidechain charge upon Ca2+ ion binding is independent of the starting net charge of the protein.
(D) Binding of Ca2+ ions to Ddx4N1 lowers the overall protein net charge. 28 ± 9 individual binding sites (negatively charged amino acid sidechains) are required to explain the change in charge observed in ELS experiments.