Figure 7.
Ddx4N0-N4 biomolecular condensates are modulated by ion binding and condensate protein charge
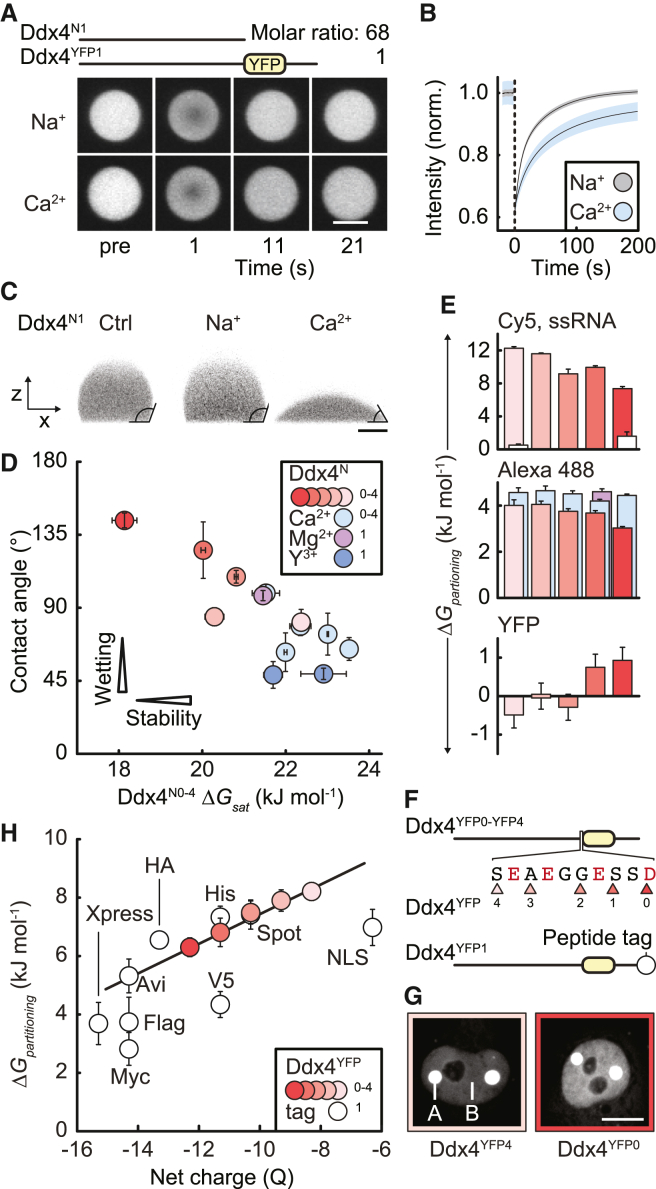
(A) FRAP experiment showing the signal originating from Ddx4YFP1 (in condensates otherwise composed of Ddx4N1) pre- and post-bleach. Molar ratio of the two proteins is indicated. Scale bar 5 μm.
(B) Mean fits of Ddx4YFP1 FRAP in the presence of additional NaCl (30 mM) or CaCl2 (10 mM). Errors indicate SEM.
(C) Images (xz plane) of Ddx4N1 condensates sitting on siliconized glass coverslips. Addition of Ca2+ ions (10 mM), but not Na+ ions (30 mM), changed Ddx4N1 condensate contact angle from >90° to <90°. Contrast is derived from Alexa 488 fluorescence. Scale bar 5 μm.
(D) Contact angles of Ddx4N0-N4 condensates in the absence and presence of additional multivalent ions (CaCl2 and MgCl2 (10 mM), YCl3 (0.5 mM)), indicated in box inset. Error bars represent SD.
(E) Partitioning of free Cy5 dye (white bars) and Cy5-labeled 24-mer single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) (top), free Alexa 488 dye (middle), and YFP (bottom) into Ddx4N0-N4 charge series condensates. Error bars represent SD. Same color scheme as in (D).
(F) Ddx4N0-N4 charge series implemented in the context of Ddx4YFP (Ddx4YFP0–YFP4). Triangles (and corresponding construct numbers) indicate the C-terminal residue of the Ddx4 sequence immediately preceding mCitrine. White circle indicates C-terminal peptide tag.
(G) Fluorescence originating from Ddx4YFP4 and Ddx4YFP0 in HeLa cell nuclei (A, condensates; B, nucleoplasm). Scale bar, 10 μm.
(H) Stability of Ddx4YFP0–YFP4 and Ddx4YFP1 with C-terminal peptide tags. Error bars indicate SD.