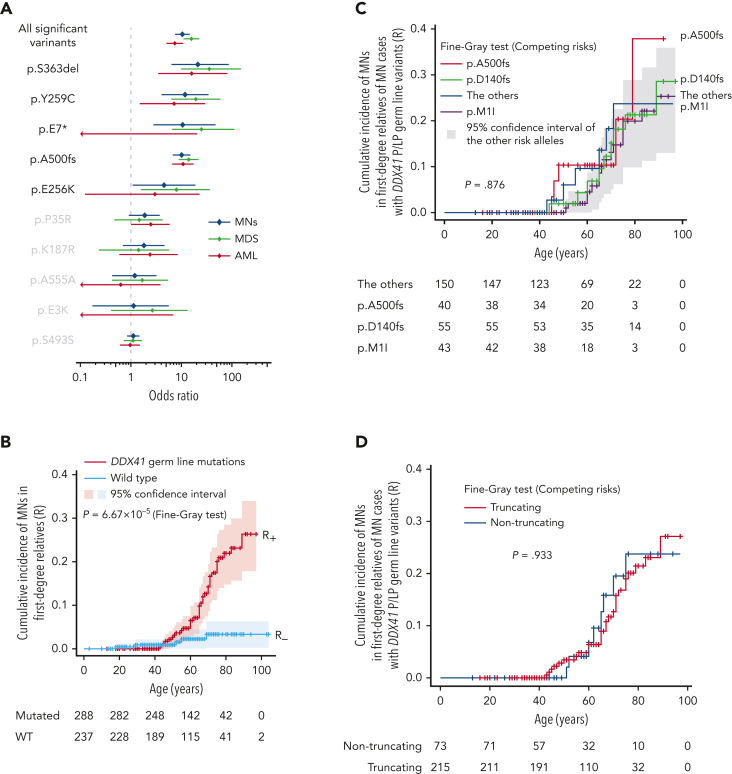
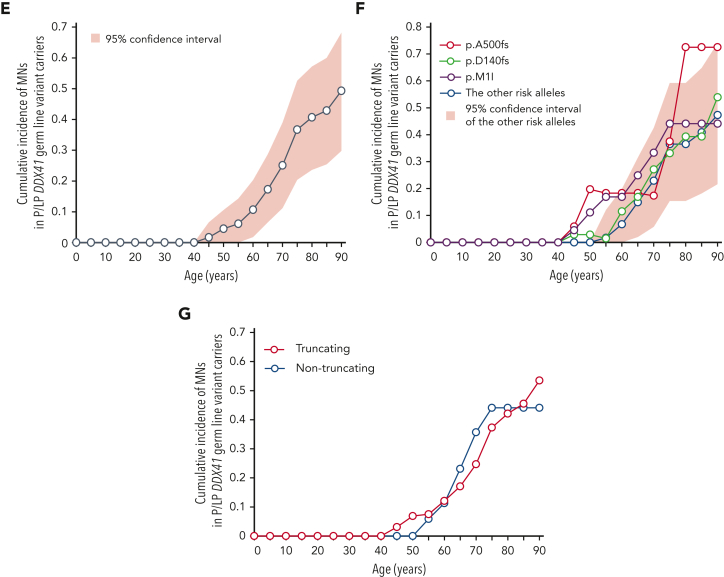
Figure 2.
DDX41-variant–associated risk of MN development. (A) Enrichment of 10 major germ line DDX41 alleles in 4461 Japanese cases with MNs compared with 20 238 cases from ethnicity-matched controls. ORs are plotted with 95% CIs for each allele. (B-D) Cumulative incidence of MNs calculated by Fine-Gray test of ages at disease onset and death in the first-degree relatives of MN cases with (red) or without (blue) germ line DDX41 mutations are shown in the whole kin cohorts (B), in each P/LP variant (C), and truncating vs nontruncating variants (D). (E-G) Cumulative incidences of MNs in carriers of DDX41 risk alleles estimated by kin-cohort analysis are demonstrated in the whole kin cohorts (E), in each P/LP variant (F), and truncating vs nontruncating variants (G).