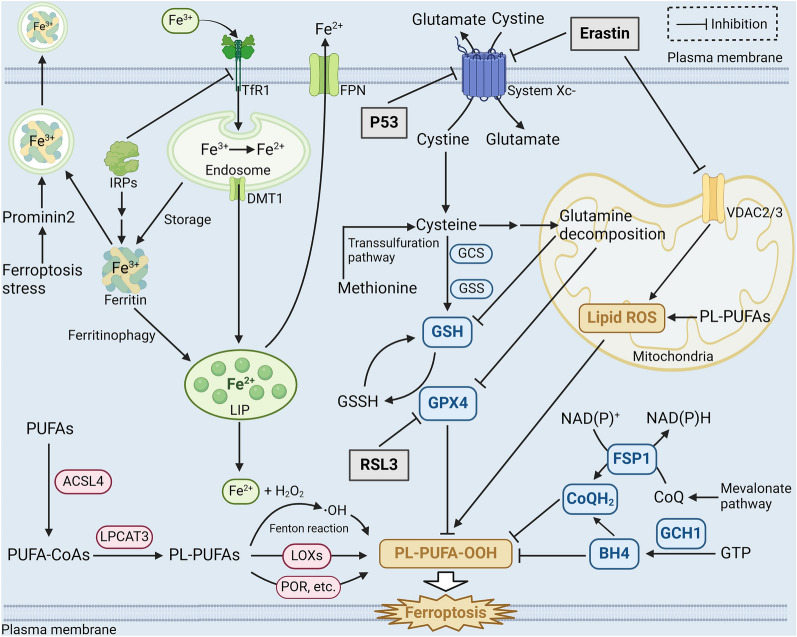
Fig. 2.
Molecular mechanism of the occurrence and regulation of ferroptosis. PUFAs are modified into PL-PUFAs, which produce lipid peroxides through the Fenton reaction involving Fe2+ or catalyzed by iron-dependent lipoxygenases (red), then attack cells to cause ferroptosis. The intracellular iron metabolism (green), three major regulatory pathways (system Xc(−)-GSH-GPX4 pathway, NADPH-FSP1-CoQ10 pathway and GCH1-BH4 pathway. blue) and mitochondrial involvement (orange) together regulate the process of ferroptosis. Three common ferroptosis inducers: erastin, RSL3, and p53 are exemplified (gray). (Created with BioRender.com.)