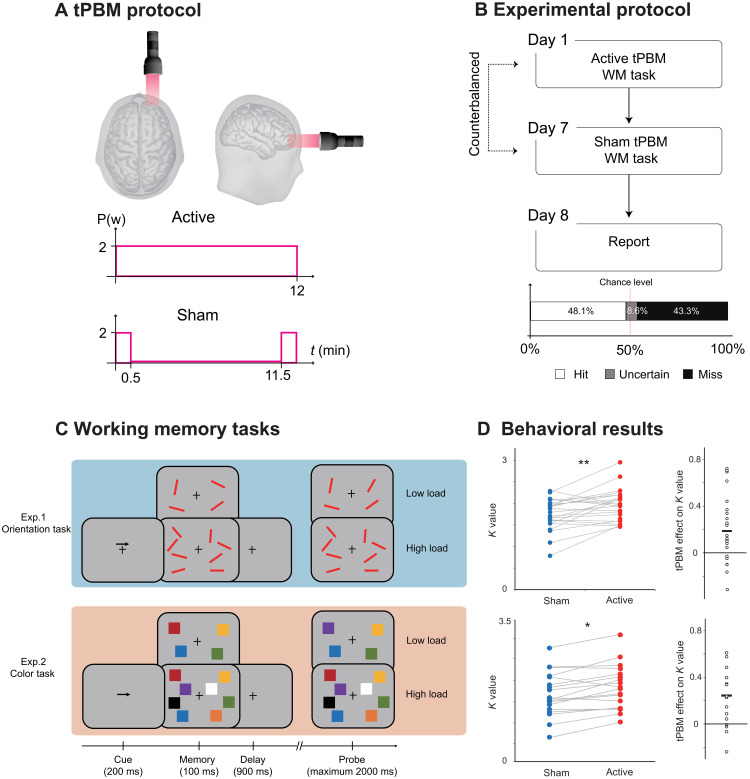
Fig. 1. Protocol, task, and behavioral results in experiments 1 and 2.
(A) tPBM protocol. Active tPBM was delivered by a laser with 1064 nm to the right PFC for a total of 12 min. (B) Experimental protocol. Each participant received two tPBM sessions (active and sham, randomized, and double-blinded design) separated by 1 week. On the eighth day, participants were required to report or guess which session involved active or sham tPBM. (C) WM tasks. In experiment 1, the participants were required to perform an orientation WM task. In experiment 2, the participant was required to perform a color WM task. Two tasks used the same relative timing and protocol, and the only difference between the two tasks was the memory dimension (orientation in experiment 1 and color in experiment 2). Each participant only participated in one experiment. (D) Left: Performance in terms of K values for orientation WM task (up) and color WM task (down) under sham tPBM (blue circles) and active tPBM (red circles). Right: The tPBM effect on the K values (active minus sham). The dots indicate individual performance. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.