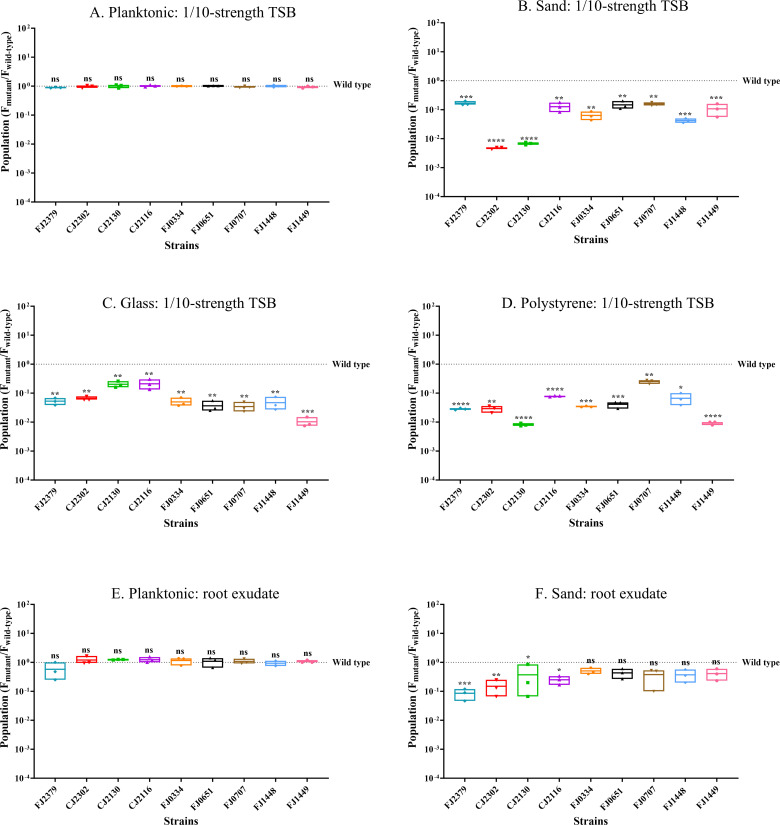
Fig 2.
Surface colonization by mutants identified in INSeq analysis. Populations of wild-type F. johnsoniae CJ1827 and deletion mutants are represented as the ratio of mutant to wild type. The initial inoculum was 106 CFU/mL of wild-type F. johnsoniae CJ1827 or mutants (FJ2379, CJ2302, CJ2130, CJ2116, FJ0334, FJ0651, FJ0707, FJ1448, and FJ1449), and populations were determined after 48 h under the following conditions: (A) planktonic: 1/10-strength TSB, (B) sand: 1/10-strength TSB, (C) glass: 1/10-strength TSB, (D) polystyrene: 1/10-strength TSB, (E) planktonic: soybean root exudate, and (F) sand: soybean root exudate. The dotted line indicates wild-type populations, and each data point in the box plots represents one biological replicate. Statistical significance was evaluated using GraphPad Prism. Differences between the mutant and wild type are indicated as ns, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.