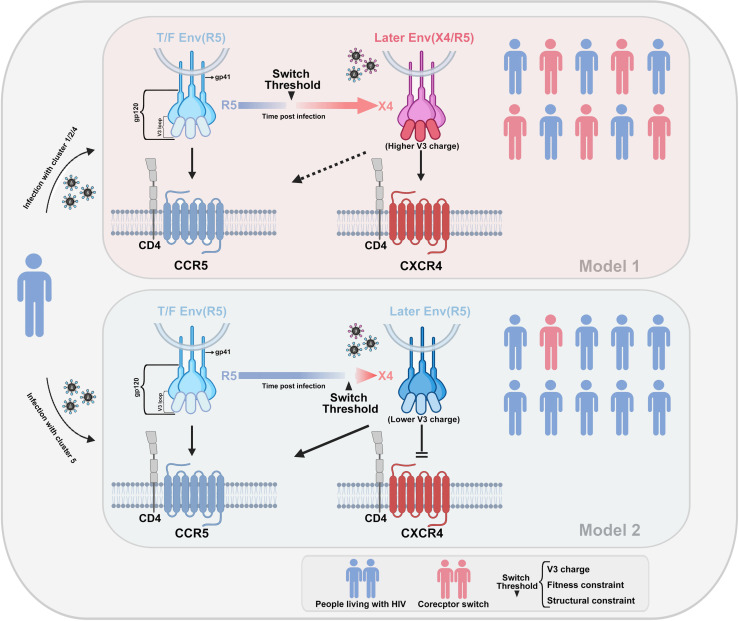
Fig 6.
Schematic representation of the molecular model of the CD4-dependent HIV co-receptor tropism switch. The co-receptor tropism of HIV is determined by the sequence of the V3 structural domain. The envelope protein gp120 of HIV interacts with the CD4+ T receptor, leading to a conformational change in the V3 loop. Depending on the amino acid sequence and structural characteristics of V3, the virus can bind to either CCR5 or CXCR4 co-receptors. Certain sub-types of viruses have a low threshold for co-receptor switching to CXCR4 tropism due to the net charge number and structural characteristics of the V3 loop. Other viruses possess a high conversion threshold and maintain CCR5 tropism, interacting with the CCR5 co-receptor over an extended period.