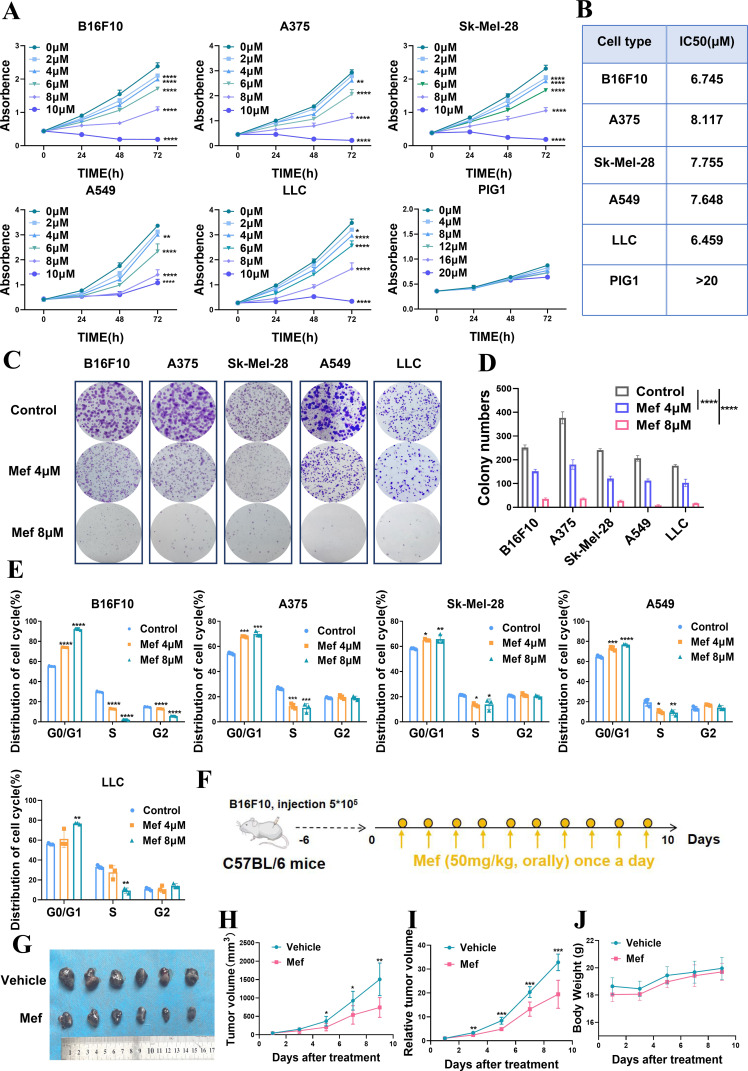
Figure 1.
Mefloquine is preferentially toxic to melanoma and lung cancer cells and impairs tumor growth. (A) The numbers of melanoma cells (A375, Sk-Mel-28, B16F10), lung cancer cells (A549, LLC) and melanocytes (PIG1) in culture supplemented with 0–20 µM Mef for 24, 48, or 72 hours were determined (n=6 replicate cultures for each cell type). (B) The IC50 values for Mef in cultures of different melanoma cell lines, lung cancer cell lines and melanocytes were determined (n=6 replicate cultures for each cell type). (C–D) A colony formation assay was used to assess melanoma and lung cancer cells after the indicated treatment (n=3 replicate cultures for each cell type). (E) Flow cytometry was used to determine the cell cycle distribution of melanoma and lung cancer cells after treatment with 0–8 µM Mef. (F–J) B16F10 tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice were treated daily with Mef (50 mg/kg, orally) to evaluate the effects on tumor volume and weight (n=6 replicate cultures for each cell type). All the data are presented as the mean (±SD). A t-test was used for comparisons between two groups. One-way analysis of variance was performed for comparisons among multiple groups. Statistical significance was assessed according to statistical methods (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; and ***p<0.001). LLC, Lewis lung cancer; Mef, mefloquine.