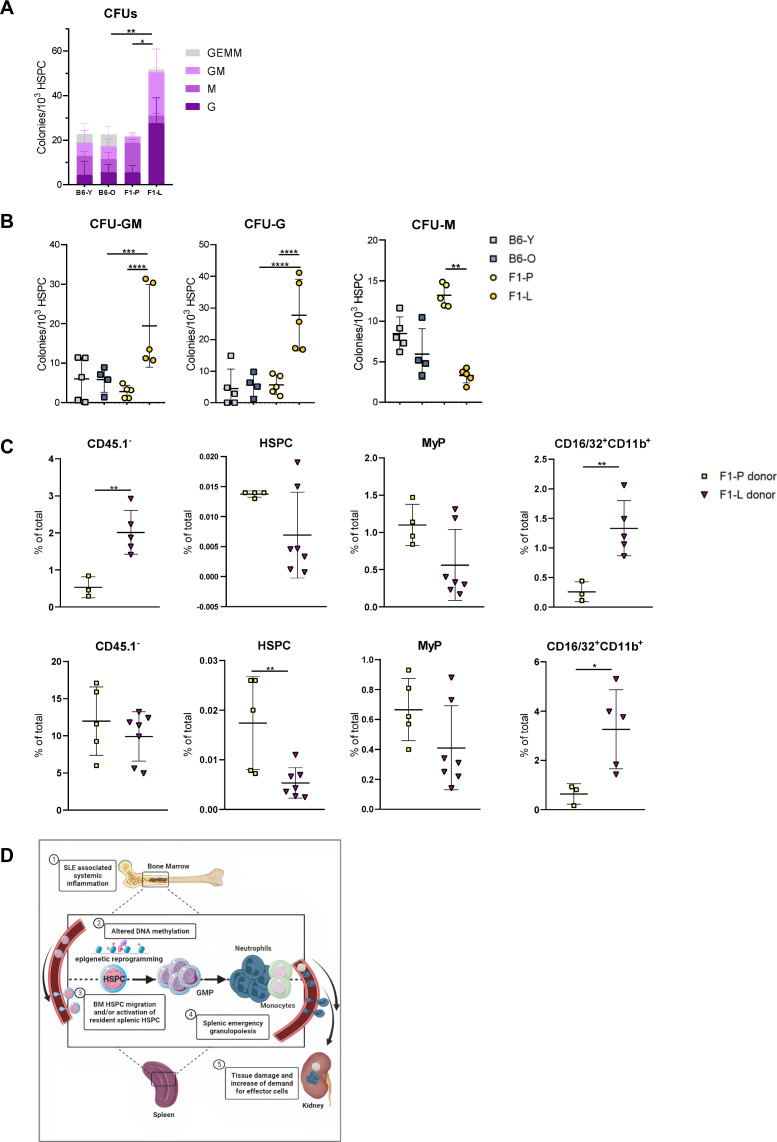
Figure 5.
Splenic extramedullary haematopoiesis is skewed towards granulopoiesis in SLE at the preclinical stage. (A) Total colonies per 103 spleen-derived HSPC (**p=0.0088; *p=0.0149). (B) CFU-G, GFU-GM and CFU-M numbers per 103 BM-derived HSPC (CFU-G: ****p<0.0001; CFU-GM: ****p<0.0001; **p=0.0002; CFU-M: **p=0.0052; n=5–6). (C) Frequencies of donor-derived (F1-P or F1-L) total cells (CD45.1-), Lin−Sca-1+c-Kit+ HSPCs, Lin−Sca-1+c-Kit− MyPs and CD16/32+CD11b+ cells in the BM (upper panels; **p=0.0096) and spleen (lower panels; **p=0.0090; *p=0.0357) of NBSGW recipients. Data are represented as mean±SD. (D) Graphical abstract showing that myeloid skewing of haematopoiesis through transcriptome and epigenetic regulation leads to migration and activation of HSPCs, resulting in emergency granulopoiesis and tissue damage in SLE. BM, bone marrow; CFU, colony-forming unit; CFU-G, CFU-granulocyte; CFU-GM, CFU-granulocyte macrophage; CFU-M, CFU-macrophage; F1-L, lupus mice; F1-P, prediseased mice; HSPC, haematopoietic stem and progenitor cell.