Figure 3.
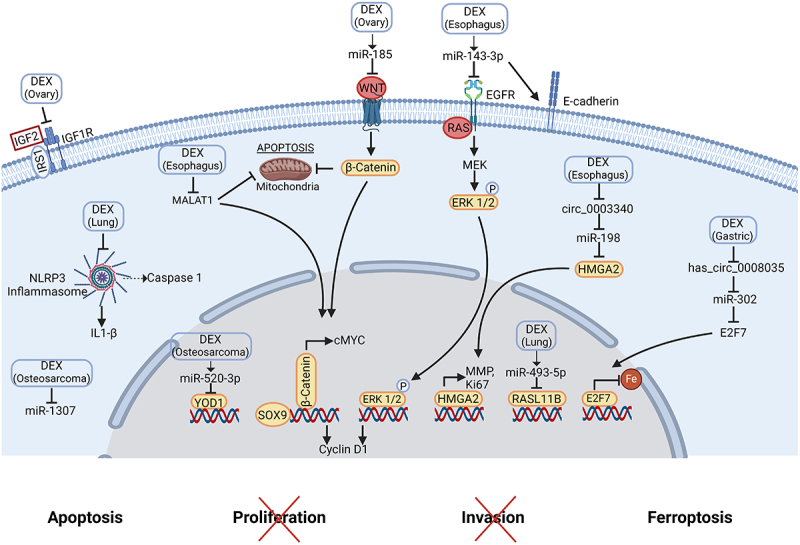
Molecular mechanisms of dexmedetomidine-mediated anti-tumor effects.
DEX suppresses esophagus cancer progression via miR-143-3p/EGFR, by repressing c-MYC, MALAT1 and ERK1/2 expression, by increasing E-cadherin expression, and by regulating circ -0003340/miR-198/HMGA2. Furthermore, DEX promotes ferroptosis in gastric adenocarcinoma through the inhibition of the circ0008035/miR-302a/E2F7 axis. It decreases the proliferation and migration of human osteosarcoma cells and triggers apoptosis via the up-regulation of miR-520a-3p that targets YOD1 and the inhibition of miR-1307. Moreover, DEX inhibits lung tumor growth and favors apoptosis via an up-regulation of miR-493-5p, which targets RASL11B and inhibits aberrant inflammasome activation. DEX induces ovarian cancer cell apoptosis via the up-regulation of miR-185 that inactivates SOX9/Wnt/B-catenin and decreases the invasion and migration by inhibiting IGF2 pathway. Created with https://www.BioRender.com
Abbreviations: DEX, dexmedetomidine; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK, extracellular regulated kinase; HMGA2, high mobility group AT-hook 2; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IL, interleukin; IRS1, insulin receptor substrate 1; MALAT1, metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3; SOX9, Sry (Sex determining region Y)-box 9
