Figure 6.
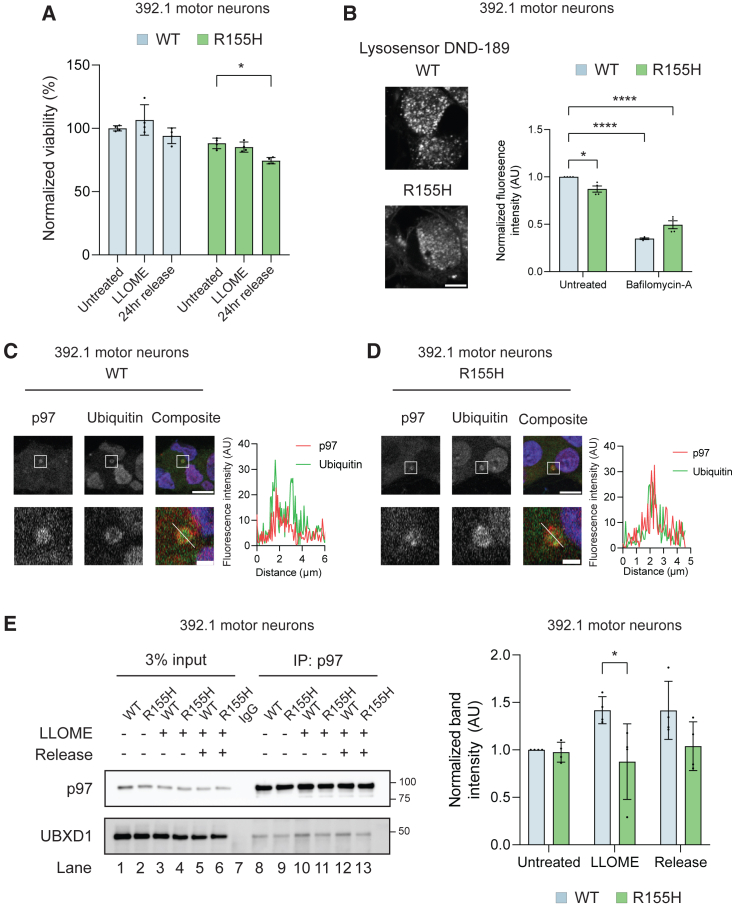
p97 R155H sensitizes motor neurons to lysosomal damage, decreases lysosomal acidity, and disrupts UBXD1 recruitment
(A) Normalized viability in 392.1 motor neurons in untreated, LLOME treated, or after release. N = 4 independent experiments.
(B) Representative images of LysoSensor DND-189 live-cell imaging in 392.1 motor neurons (left). Quantification of DND-189 fluorescence in untreated and bafilomycin-A treated cells. N = 4 independent experiments. Scale bar, 5 μm.
(C and D) Representative images of wild-type (C) and p97 R155H (D) 392.1 motor neurons co-stained with p97 and ubiquitin showing colocalization (left). Line graph of the fluorescence intensity of p97 and ubiquitin as indicated in the bottom right image panel. N = 3 independent experiments. Scale bars, 10 μm (upper panels) and 1 μm (lower panels).
(E) Immunoblot of endogenous p97 immunoprecipitation in 392.1 motor neurons before, during, and after LLOME treatment (left). Release condition represents 5 h of recovery. Quantification of UBXD1 band intensities normalized to immunoprecipitated p97 (left). Data expressed as normalized band intensities ±SD. N = 4 independent experiments. All data expressed as means ± SEM unless otherwise indicated. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s (A) or Sidak’s (B, E) multiple comparison test. See also Figure S6.