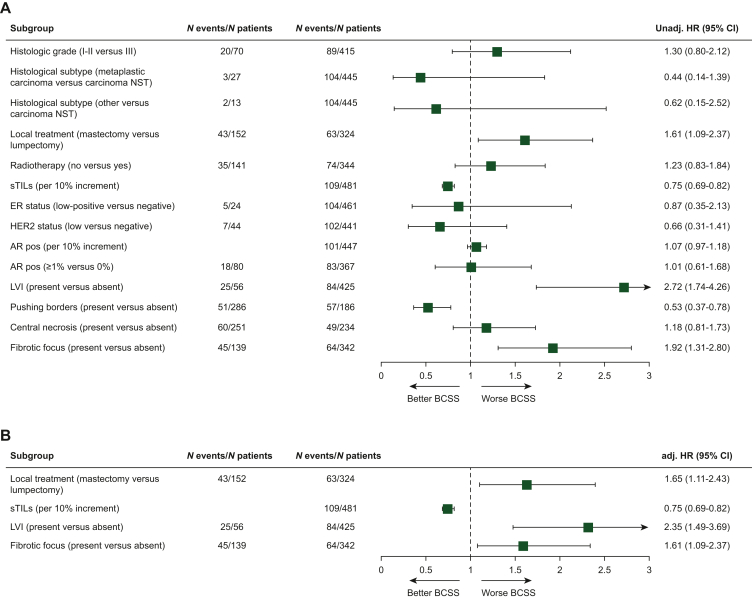
Figure 2.
Unadjusted and adjusted HRs for BCSS among young patients with node-negative triple-negative breast cancer by tumor characteristics. (A) Plot of unadjusted hazard ratios (unadj. HR) and (B) adjusted hazard ratios (adj. HR) for BCSS comparing young (<40 years) patients with a specific tumor characteristic (depicted in the figure) versus those without that specific characteristic. For every tumor characteristic separately a (A) univariable and (B) multivariable Cox proportional hazards model was built. In the multivariable models, HRs were adjusted for local treatment (lumpectomy, mastectomy, surgery not specified), sTILs (per 10% increment) and LVI (absent, present), unless otherwise specified. Models for sTILs and LVI as the covariate of interest were adjusted for local treatment (lumpectomy, mastectomy, surgery not specified) and LVI (absent, present) or sTILs (per 10% increment), respectively. T-stage (1/2, 3) and grade (1/2, 3) were not detected as prognostic or confounding variables and therefore not included in the multivariable models. The group with the highest number of events was used as the reference group. sTILs and AR positive were used as continuous variables with HR showing change in risk per 10% increment. Patients with unknown values were omitted. The square shows unadj./ adj. HR and its size reflects the number of patients included, while whiskers represent the 95% CI. AR, androgen receptor; BCSS, breast cancer-specific survival; CI, confidence interval; ER, estrogen receptor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; LVI, lymphovascular invasion; NST, carcinoma of no special type; sTILs, stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.