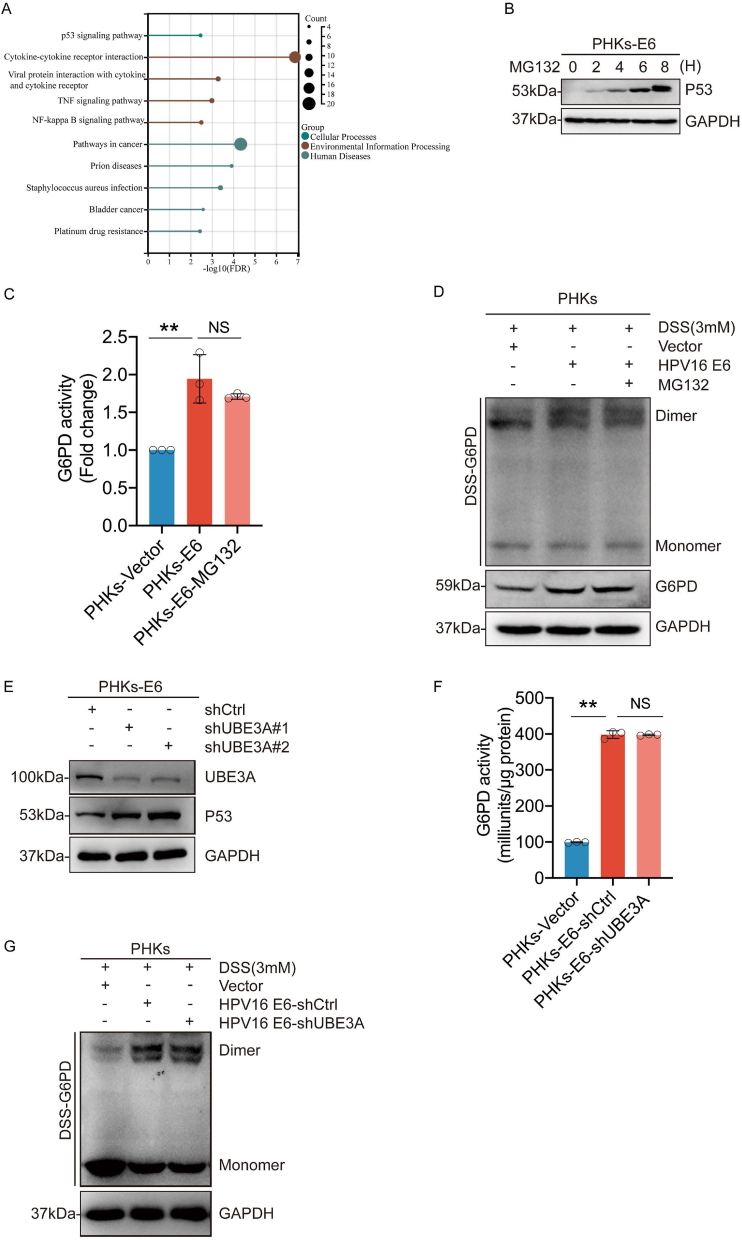
Fig. 5.
HPV16 E6 regulates G6PD enzyme activity independent of p53. (A) KEGG enrichment analysis of the differential genes screened based on GEO (GSE58841). (B) PHKs-E6 cells were treated with 5 μM MG132 for the indicated duration. The whole-cell extracts (WCEs) were then collected for immunoblotting to detect p53 levels in the cells. (C) G6PD enzyme activity was assayed after treating PHKs-E6 cells with MG132 (5 μM) for 6 h. (D) PHKs-E6 cells were treated with 5 μM of MG132 for 6 h. Cells were harvested and crosslinked using DSS (3 mM), followed by western blotting with an anti-G6PD antibody. (E) PHKs-E6 cells were stably transduced with lentiviruses expressing shUBE3A. WCEs were analyzed via immunoblotting for UBE3A and p53. (F) PHKs-E6-shUBE3A cells were employed for the detection of G6PD enzyme activity. (G) Crosslinking with DSS followed by immunoblotting to detect dimeric and monomeric G6PD. Each dot represents an independent biological replicate in the plots. Data are presented as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01 compared with indicated groups. Statistical significance was determined using unpaired two-tailed t-test. NS, not significant. HPV, human papilloma virus; G6PD, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; DSS, disuccinimidyl suberate.