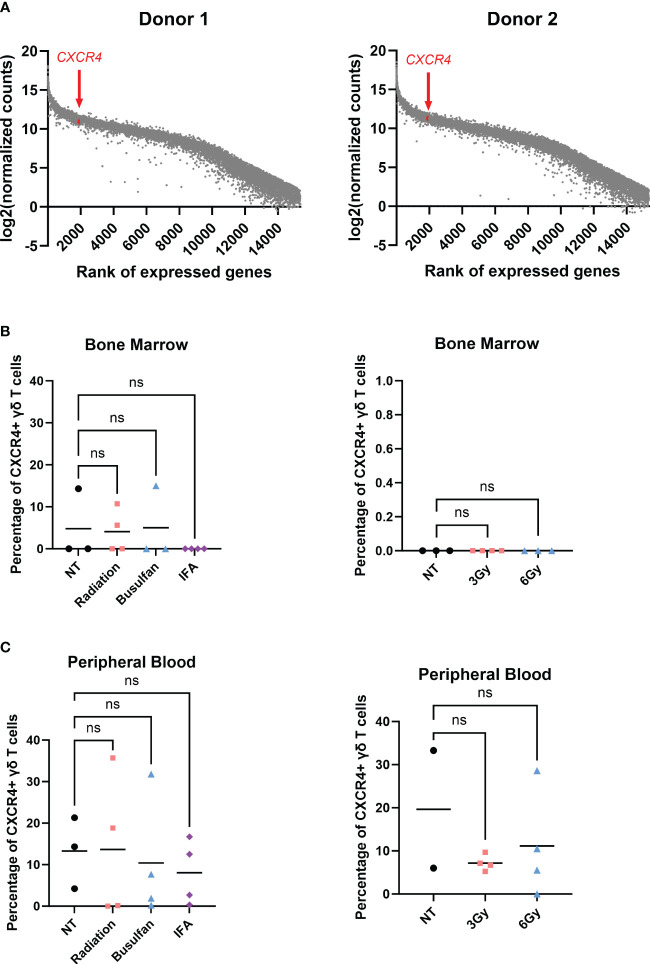
Figure 3.
γδ T cells do not migrate to the bone marrow via the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis. (A) RNA-seq performed on two individual biological replicates of γδ T cells isolated from two different PBMC donors; genes were ranked, and log2(normalized counts) was calculated; CXCR4 highlighted in red. (B) Mice were conditioned with 1.5-Gy radiation, 25 mg/kg busulfan, or 300 µL IFA (1:1 with PBS) or 3-Gy or 6-Gy radiation and then systemically infused with γδ T cells; 24 hours later, bone marrow and (C) blood were harvested and assessed for live CXCR4+ γδ T cells via flow cytometry using the CXCR4 BV480 antibody. For NT, n = 2–3 mice, and n = 4 for conditioned mice (B, C). (B, C) Statistics analyzed by non-parametric one-way ANOVA with post hoc (p> 0.05 = ns), ns, not significant, and the sample mean is denoted with a black line. RNA-seq, RNA sequencing; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; IFA, incomplete Freund’s adjuvant; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.