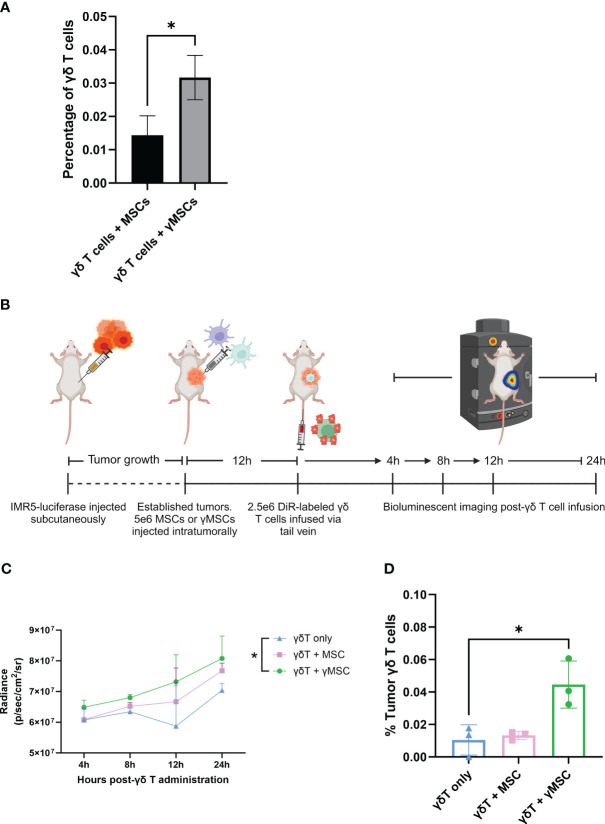
Figure 6.
γδ T cells can be recruited to bone marrow and tumors through chemoattractant relationships. (A) NSG mice (n = 3 per condition) were conditioned with 1.5-Gy TBI 24 hours prior to intraosseous injection of 1.6e5 MSCs or γMSCs. After 24 hours, γδ T cells were injected retro-orbitally. Twenty-four hours later, femurs were harvested and stained for flow cytometry. The percentage of γδ T cells was then calculated. Error bars represent standard deviation. Statistical significance was analyzed by Student’s t-test (p< 0.05 = *). (B) Schematic of experiment. Mice were injected with IMR5-luciferase cells; tumors were established, and MSCs or γMSCs were injected intratumorally. n = 3 mice per condition. Twelve hours later, DiR-labeled γδ T cells were injected via the tail vein, and migration in vivo was monitored over 24 hours through relative bioluminescence. (C) Bioluminescent quantitative analysis of γδ T-cell trafficking to tumor over 24 hours. Statistics analyzed by paired t-test with Bonferroni correction (p< 0.05 = *). (D) Flow cytometry analysis of the percentage of γδ T cells per tumor 24 hours post-infusion. Statistics analyzed by paired t-test with Bonferroni correction (p< 0.05 = *), and error bars represent standard deviation. TBI, total body irradiation; MSCs, mesenchymal stromal cells.