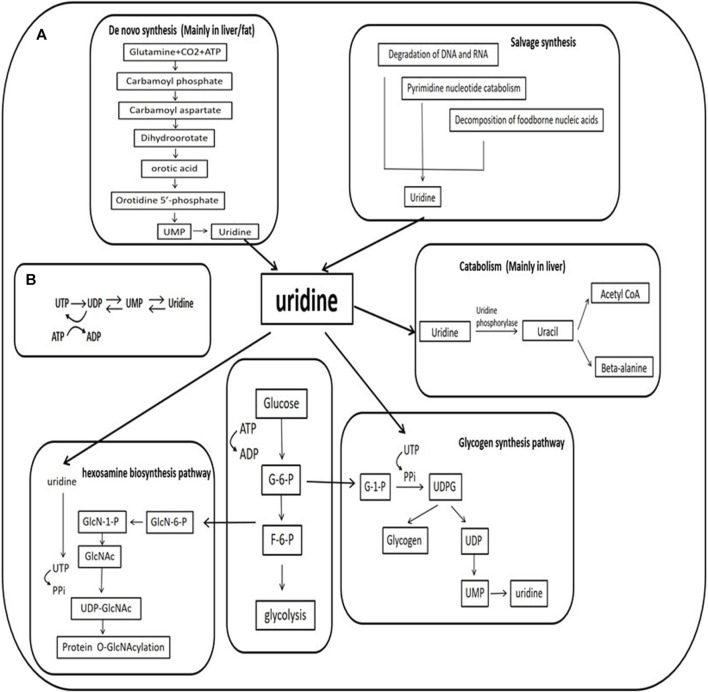
FIGURE 1.
Uridine and its metabolism (A). The mechanism of uridine synthesis and catabolism and the role of uridine in the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway and glycogen synthesis (B). Relationship between ATP consumption and uridine. UTP is produced by the phosphorylation of UDP with ATP used as phosphate donor, a decrease in ATP concentration results in decreased phosphorylation of UDP to UTP, leading to increased UDP and uridine-5′-monophosphate (UMP). These changes accelerate the degradation of uracil nucleotides (UTP→UDP→UMP→ uridine). G-6-P: glucose-6-phosphate; F-6-P: fructose-6-phosphate; GlcN:glucosamine; GlcNAc:N-acetyl glucosamine; UDP:uridine-5′-diphosphate; UTP:uridine-5′-triphosphate; PPi:inorganic pyrophosphate; ADP:cytidine -5′-diphosphate; ATP:cytidine -5′-triphosphate.