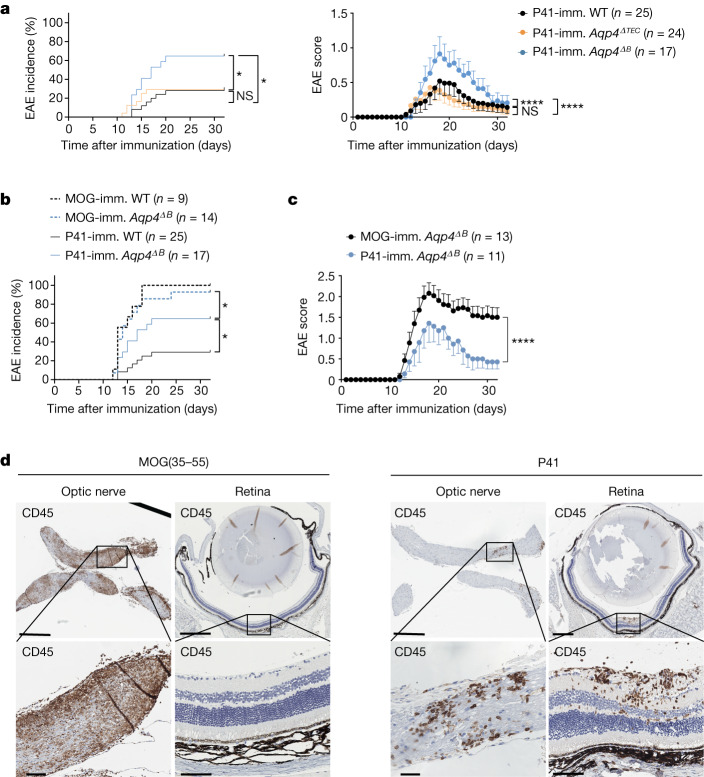
Fig. 5. AQP4-specific T cell precursor frequencies in Aqp4ΔB mice, but not in Aqp4ΔTEC mice, are sufficient to cause overt autoimmune disease in response to an antigen-specific trigger.
In contrast to WT mice and Aqp4ΔTEC mice, Aqp4ΔB mice were susceptible to EAE after immunization with P41 in CFA (see also Extended Data Fig. 6a–c). a, EAE incidence (left) and mean ± s.e.m. disease severity (right) in all P41-immunized WT, Aqp4ΔTEC and Aqp4ΔB mice. b, EAE incidence in all MOG(35–55)-immunized and P41-immunized WT mice and Aqp4ΔB mice. c, The mean ± s.e.m. disease severity in clinically sick MOG(35–55)-immunized and clinically sick P41-immunized Aqp4ΔB mice. Statistical analysis was performed using Mantel–Cox log-rank tests and two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post test to compare incidences and disease course, respectively. Only the relevant tests are indicated in b for legibility. d, Representative CD45 stainings of the optic nerve and retina in MOG(35–55)-immunized (left) and P41-immunized Aqp4ΔB mice (right) at the peak of EAE. n = 2 independent experiments. Scale bars, 500 µm (top) and 50 µm (bottom).