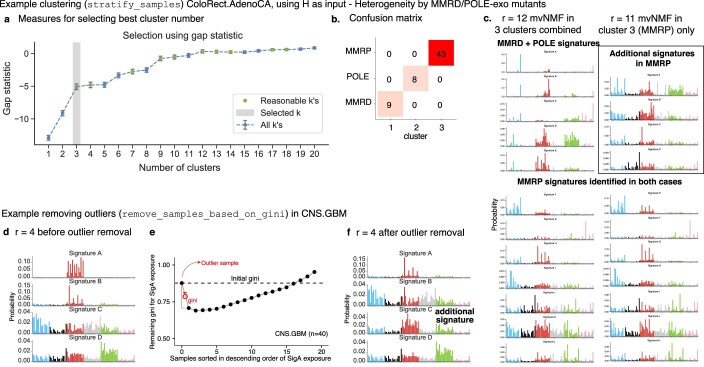
Extended Data Fig. 6. Examples illustrating cohort stratification and outlier removal with the preprocessing module.
a-c. An example with the PCAWG ColoRect.AdenoCA dataset to demonstrate that cohort stratification can benefit de novo signature discovery. After an initial signature discovery with the entire dataset of 60 samples, hierarchical clustering is performed using the de novo exposure matrix H, and 3 clusters are selected by the gap statistic, as shown in panel (a). The 3 clusters correspond to samples with MMRP, MMRD, and POLE mutations, respectively, as shown in panel (b). In panel (c), de novo signatures discovered from the entire dataset of 60 samples and the MMRP cluster (43 samples) are plotted, demonstrating improved sensitivity of signature discovery after cohort stratification. Specifically, 12 signatures are discovered when de novo discovery is performed with the entire dataset of 60 samples, while 11 are discovered with the MMRP cluster alone. Out of the 11 MMRP-specific signatures, only 7 are discovered before cohort stratification. Therefore, a separate run of de novo discovery with the MMRP cluster allows 4 more MMRP-specific signatures to be discovered. In panel (a), reasonable k means any k satisfying Gap(k)≥Gap(k + 1) − sk+1, where Gap(k) denotes the gap statistic (indicated by dots in the plot) and sk the standard deviation of 50 independent simulations after accounting for simulation errors (indicated by error bars in the plot). The smallest reasonable k is chosen as the optimal k. See60,61 for more details. d-f. An example with the PCAWG CNS.GBM dataset to demonstrate that outlier removal can benefit de novo signature discovery. When signature discovery is performed with the entire dataset, 4 de novo signatures are discovered, as shown in panel (d), where Signature A corresponds to SBS11 associated with temozolomide treatment. When the de novo exposures are inspected with the Gini coefficient, a single outlier sample with an exceptionally strong exposure of Signature A is detected, as shown in panel (e). After removing this outlier and rerunning signature discovery with the remaining samples, an additional signature is discovered, as shown in panel (f), demonstrating improved sensitivity.