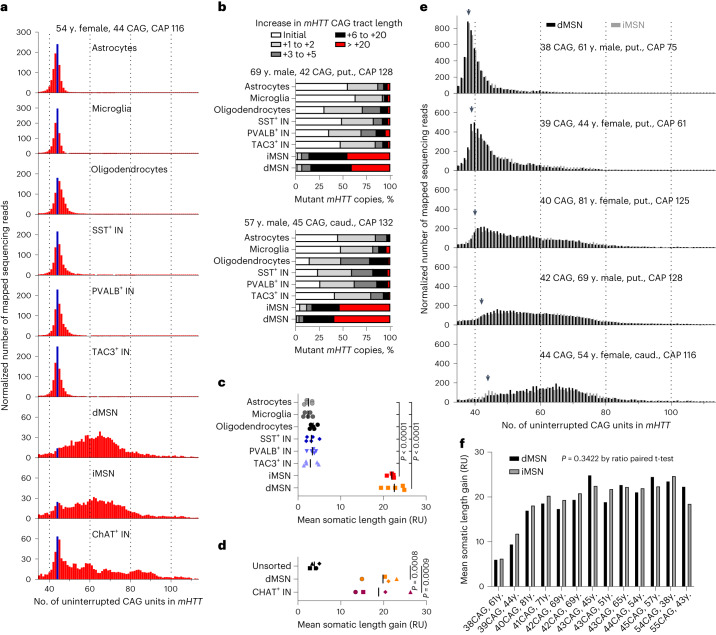
Fig. 3. mHTT CAG tract undergoes somatic expansion in selected striatal neuron types.
a, Length distribution of mHTT CAG tract in studied cell types of caudate nucleus and putamen of a 54-year-old female donor that carried a tract of 44 uninterrupted CAG units. Blue bar marks sequencing reads derived from the initial unexpanded CAG tract. y axes denote normalized number of sequencing reads mapped to reference sequences with different CAG tract lengths (normalized by scaling to 1,000 reads). Reads derived from the normal HTT allele are not shown. b, Frequency distribution of mHTT copies with different CAG tract length increases. Data are shown for striatal cell types of two donors that carried the most common HD-causing CAG tract lengths. c,d, Comparison of mean somatic length gain (measured in repeat units (RUs)). c, Although the mean somatic length gain of mHTT CAG tract was not different between dMSN and iMSN, comparison of each of these to any other striatal cell type showed a statistically significant difference (n = 5 individuals, P < 0.0001 by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), adjusted P < 0.0001 in Holm–Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). d, The mean somatic length gain of mHTT CAG tract was not different between dMSNs and CHAT+ interneurons, but comparison of each of these to unsorted nuclei showed a statistically significant difference (n = 4 individuals, P = 0.0004 by one-way ANOVA, adjusted P < 0.001 in Holm–Sidak’s multiple comparisons test). Different symbols are used for each of the four donors. e, Length distribution of mHTT CAG tract in MSNs of caudate nucleus and putamen in donors carrying mHTT alleles of reduced and full penetrance. Arrowhead indicates the initial unexpanded size of the CAG tract. f, Comparison of the mean somatic length gain of mHTT CAG tract. n = 13 individuals, P = 0.3422 between cell types, in ratio paired t-test (two sided). caud., caudate nucleus; put., putamen; y., year-old.