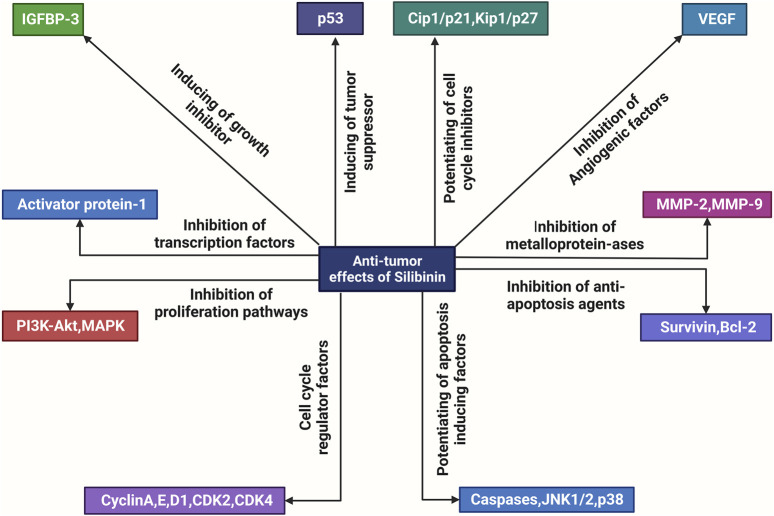
FIGURE 1.
An overview of the molecular mechanisms underlying the anti-tumor actions of silibinin. Silibinin exerts a direct inhibitory effect on various factors involved in cell division and proliferation, including metalloproteinases (MMPs), anti-apoptosis proteins such as Bcl-2, growth factors such as Flt, VEGF, AR, PSA, and IGF, cell mitogen controllers such as PI3K, Akt, MAPK, cell cycle regulators such as the CDK family and pSTAT3. Additionally, it enhances the activity of apoptotic inducers such as JNK (c-Jun N-terminal kinases), Cip and Kip families, and growth inhibitors such as IGFBP. Consequently, silibinin exhibits anti-tumor effects.