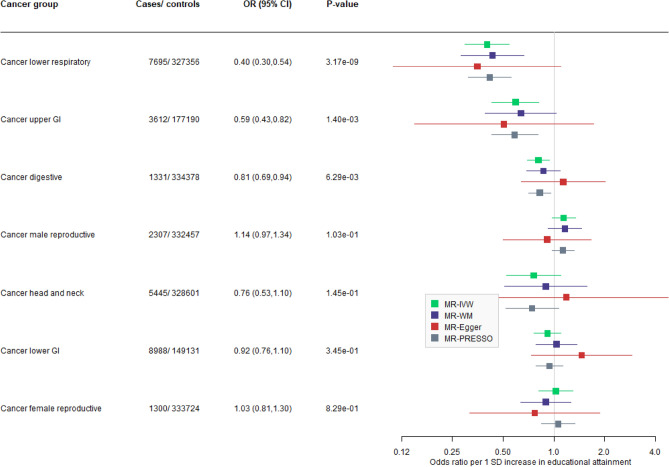
Figure 2.
Two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) estimates per 1 standard deviation increase in educational attainment for 7 cancer groups: digestive, female reproductive, head and neck, lower respiratory, lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract, male reproductive and upper GI tract. Associations were considered statistically significant if MR-IVW and MR-PRESSO p-values were smaller than 0.05/7 = 7.14 × 10–3, MR-Egger and MR-weighted median effect estimates were in the same direction and the MR-Egger intercept was not significant (p > 0.05).