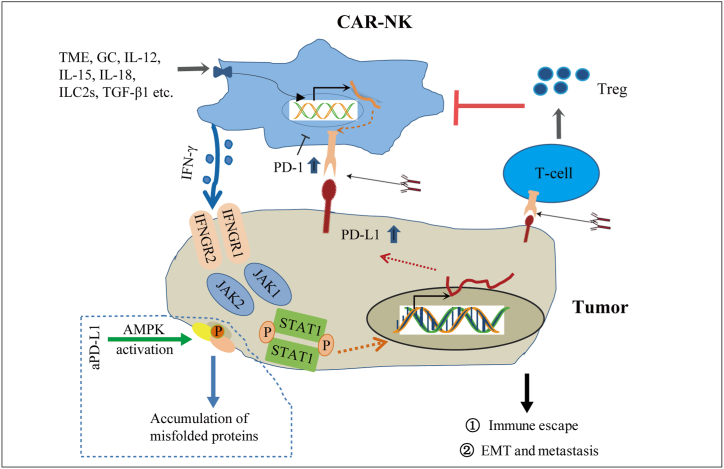
Fig. 4.
Depict the mechanism of the interaction between tumor cells and NK cells. NK cells bind to target cells, secrete IFN-γ, up-regulate PD-L1 on target cells through JAK/STAT pathway, directly inhibit the function of NK cells through binding with PD-1, or indirectly enhance tumor resistance to NK cells through Treg cells, thus promoting tumor immune escape. In addition, PD-L1, GC, interleukin, TGF and other factors in the tumor microenvironment can induce the up-regulation of PD-1 on NK cells. PD-1/PD-L1 antibody can inhibit the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1, and blocking PD-L1 may activate AMPK and enhance the sensitivity of tumor to NK cells.